AWS Lambda is validated for use with Wasabi S3 as the backend. Lambda can be used as a virtual function that you can run on demand, and it can scale automatically.
You can integrate this service and use Wasabi S3 to store and manage your data. You can create a Lambda function to trigger events in various programming languages. Since the Lambda function requires IAM roles to operate, below is a demonstration of how to create an IAM role and a Lambda function to communicate with Wasabi.
Inserting a JSON File in Wasabi S3 Using a Lambda Function
Log in to your Wasabi account and create a new bucket or use an existing one. For this example, we have created a new bucket called ‘lambda-wasabi' in the us-east-2 region. You can choose any name and region you prefer.
Create an IAM user that has (at a minimum) s3:PutObject permissions for the bucket (‘lambda-wasabi’ in this example).
Create a Lambda function in AWS that uses the Wasabi S3 bucket from Step 1, and the Wasabi IAM user from Step 2.
If you have not worked with IAM Policies and Roles previously, it is highly recommended that you go through the official documentation and practice on the console.
Creating a Wasabi Permission Policy
Log in to your Wasabi account, navigate to the Policies section, and click Create Policy.
Enter a policy name. For this example, use the name lambda-user-policy and allow the permission s3:PutObject.
"Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "VisualEditor0", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "s3:PutObject", "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::wasabi-lambda/*" } ] }Save the policy.
Creating a User in Wasabi
Log in to your Wasabi account, navigate to Users, and click Create User.
Enter a username. For this example, use the name wasabi-lambda-user.
In the Type of access field, check Programmatic, then click Next.
Leave the Group field blank.
Add the permissions policy previously created.
Generate the access keys and keep them in a secure location for future use.
Creating the Lambda Function
Go to the Lambda service in your AWS account, select Functions, and then click Create Function.
.png)
Enter a function name. For this example, use the name lambda-wasabi-test.
Choose the Runtime language Python 3.12.
Choose the Architecture x86_64.
Choose the Permissions role to Create a new role with basic Lambda permissions.
.png)
Upload or paste your Lambda function code in the Function code box, for example.
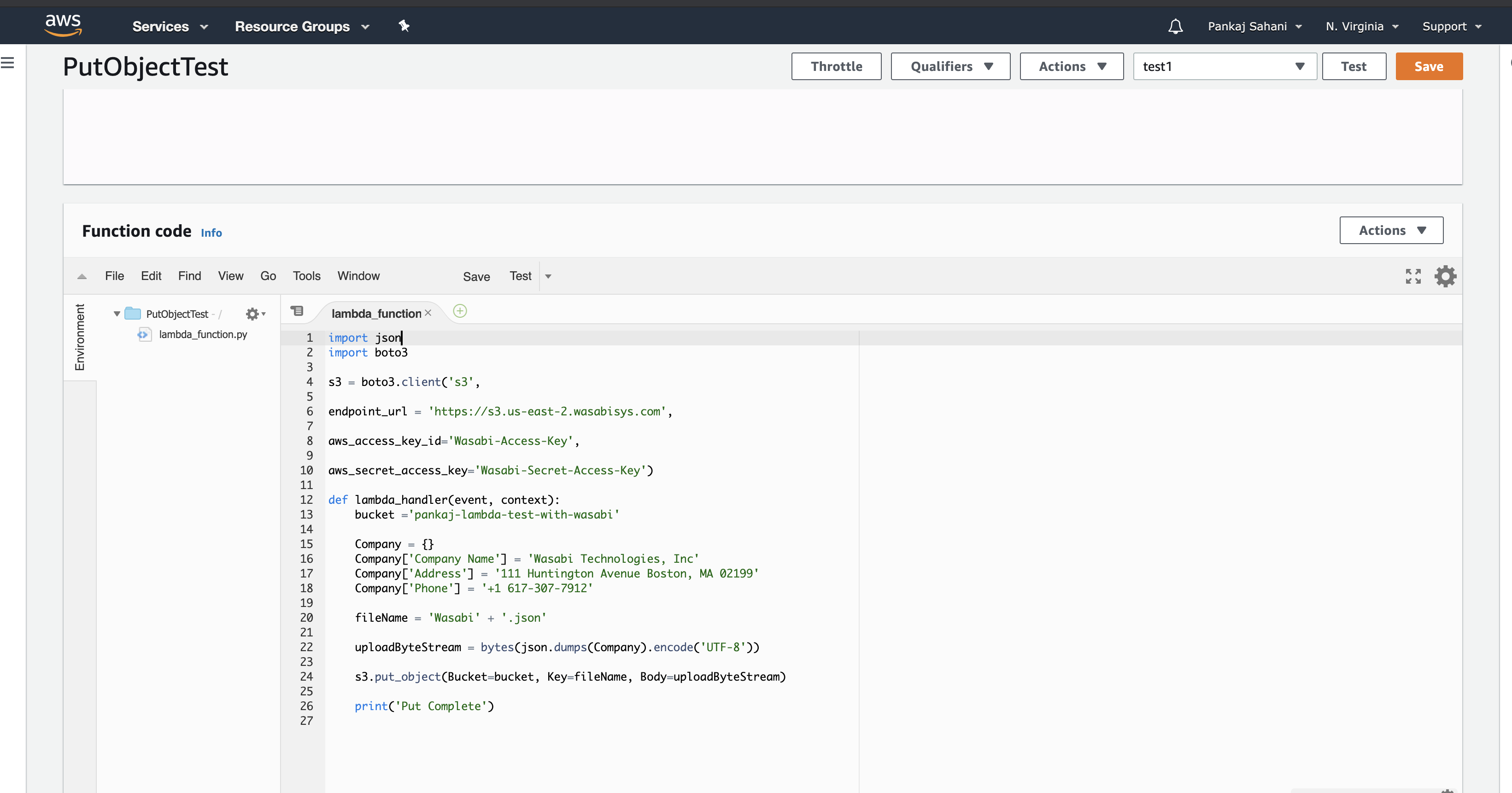
The actual function code is shown below.
import json import boto3 s3 = boto3.client('s3', endpoint_url='https://s3.wasabisys.com', aws_access_key_id='Wasabi-Access-Key', aws_secret_access_key='Wasabi-Secret-Key') def lambda_handler(event, context): bucket = 'lambda-wasabi' Company = {} Company['Company Name'] = 'Wasabi Technologies LLC' Company['Address'] = '75 Arlington Street Suite 810, Boston, MA 02116' Company['Phone'] = '+1 617-307-7912' fileName = 'Wasabi.json' uploadByteStream = bytes(json.dumps(Company).encode('UTF-8')) s3.put_object(Bucket=bucket, Key=fileName, Body=uploadByteStream) print('Put Complete')This code uses Wasabi’s us-east-2 storage region. To use other Wasabi storage regions, use the appropriate Wasabi URL. The access keys used must be those generated previously.
Once the function code is uploaded, typed, or pasted, click Deploy.
Once the code is successfully deployed, select the Test tab near the bottom of the page. In the Test event section, enter an event name and click Test.
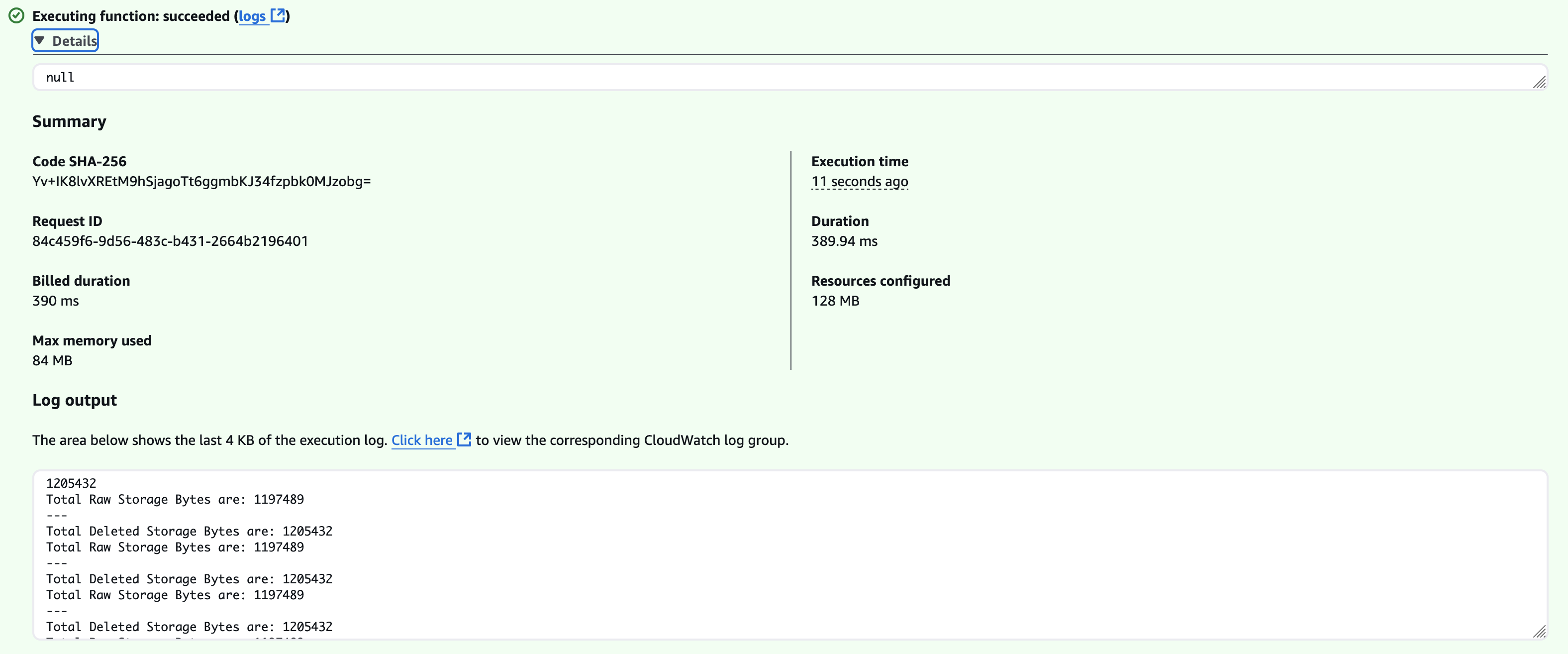
Once the test is run, you should see that the execution succeeds. If any failures occur, Lambda will provide a detailed error output.
.png)
This function has successfully triggered an event to Wasabi S3 and inserted a JSON document specified by the code, as shown below.
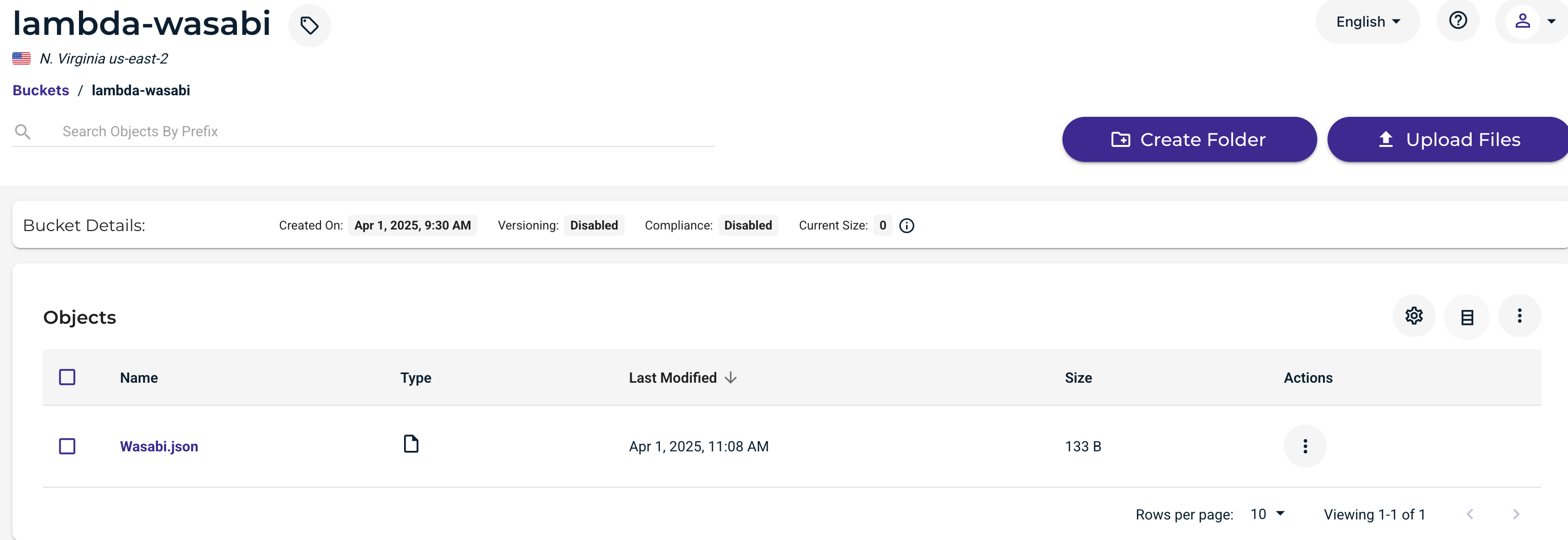
Reading From a File Stored in Wasabi S3 Using a Lambda Function
Consider a scenario where you have a large file with data, and you want to parse through its content to read only the specific data you need for your use case using a Lambda function.
For this example, we are using the same bucket from earlier called "lambda-wasabi" in the us-east-2 region. Our sample file is shown below, and you can download this file at the bottom of this article for reference.
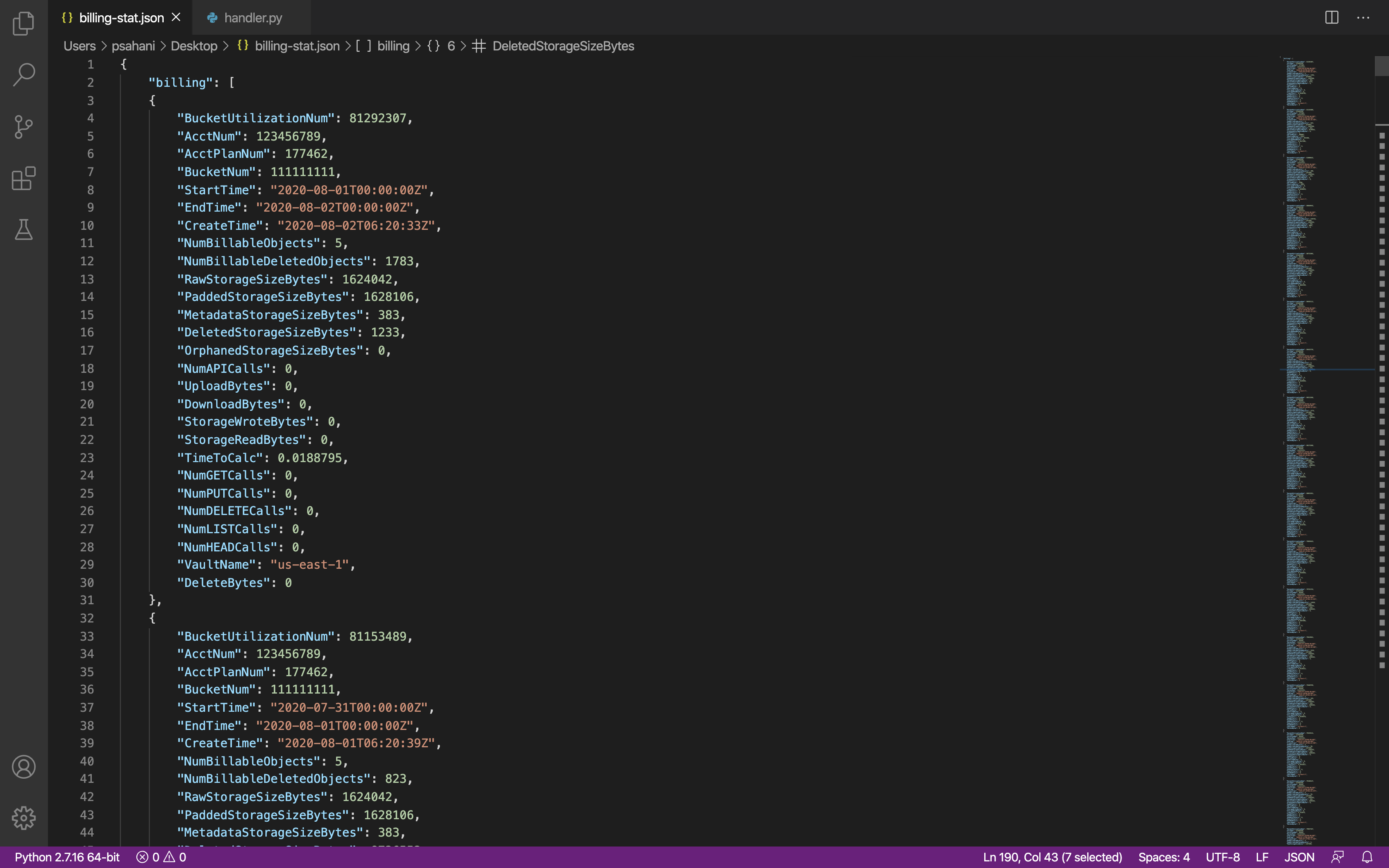
Our goal with this Lambda function is to only retrieve:
Total Deleted Storage Bytes
Total Raw Storage Bytes
Create a bucket in your Wasabi account and upload the data file.
Create a permission policy. Click Create Policy and enter the name lambda-user-policy, allowing s3:GetObject permissions.
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "VisualEditor0", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "s3:GetObject", "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::wasabi-lambda/*" } ] }Click Save.
We can then create this user in Wasabi
Log into your Wasabi account, go to Users and click on Create User
Give the user a name (we’ll use ‘wasabi-lambda-user' for this example)
Check “Programmatic” under “Type of access” and click Next
Skip adding to a group
Add the permissions policy created above to the user
Create User and store the access/secret key pair in a safe place (we will be using it for the Lambda function)
Create Lambda function:
Go to Lambda service in your AWS account and click on "create functions"
Give this function a name: we are naming it "QueryingWasabiS3"
Runtime: we are using Python 3.12, you can choose any language are you writing lambda function in
Permissions: Allow AWS to create a new role with basic Lambda permissions
Click the ‘Create Function’ button
.png)
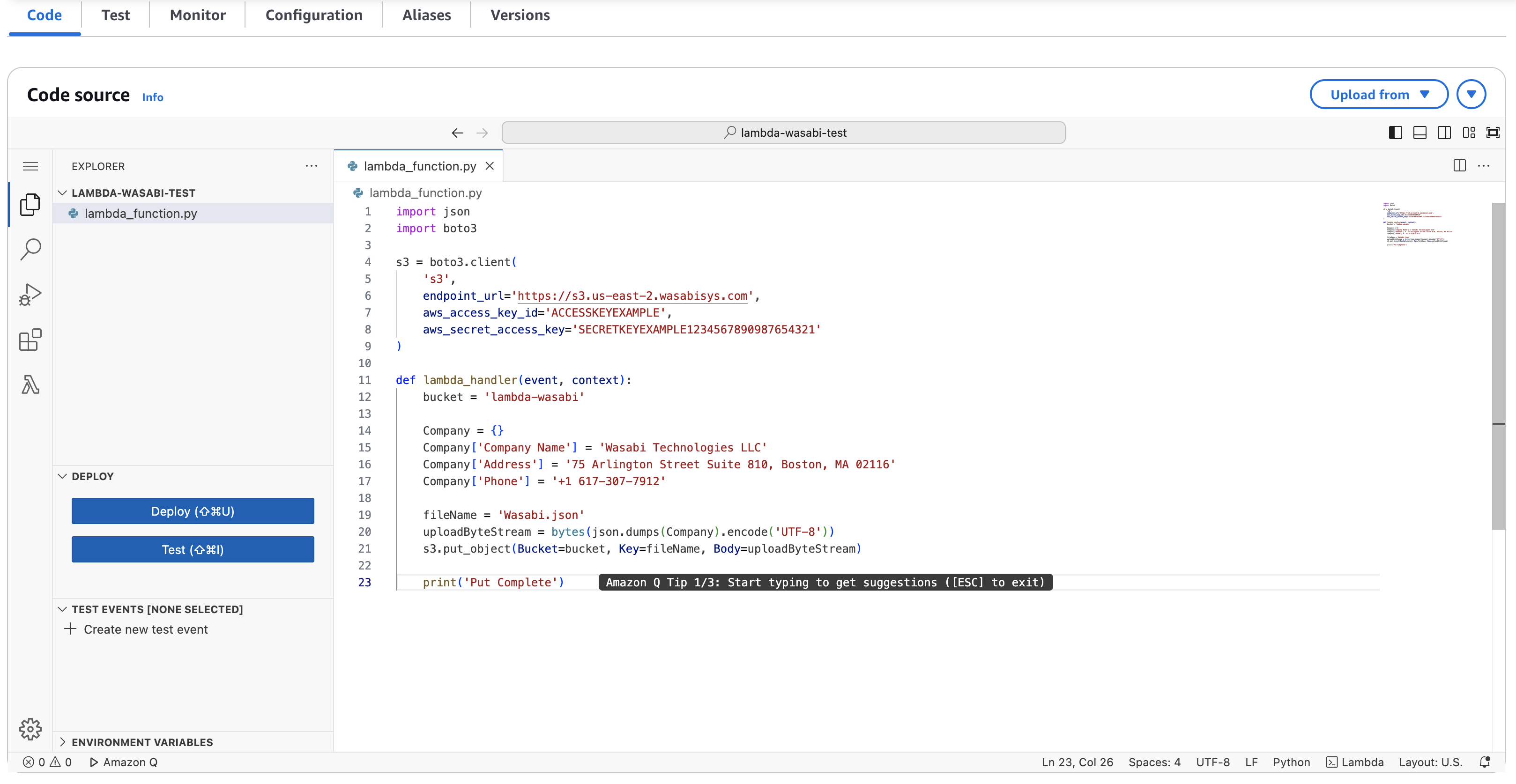
Now, upload your own lambda function code or you can paste your code in the box
Below is a sample code example which we are using:
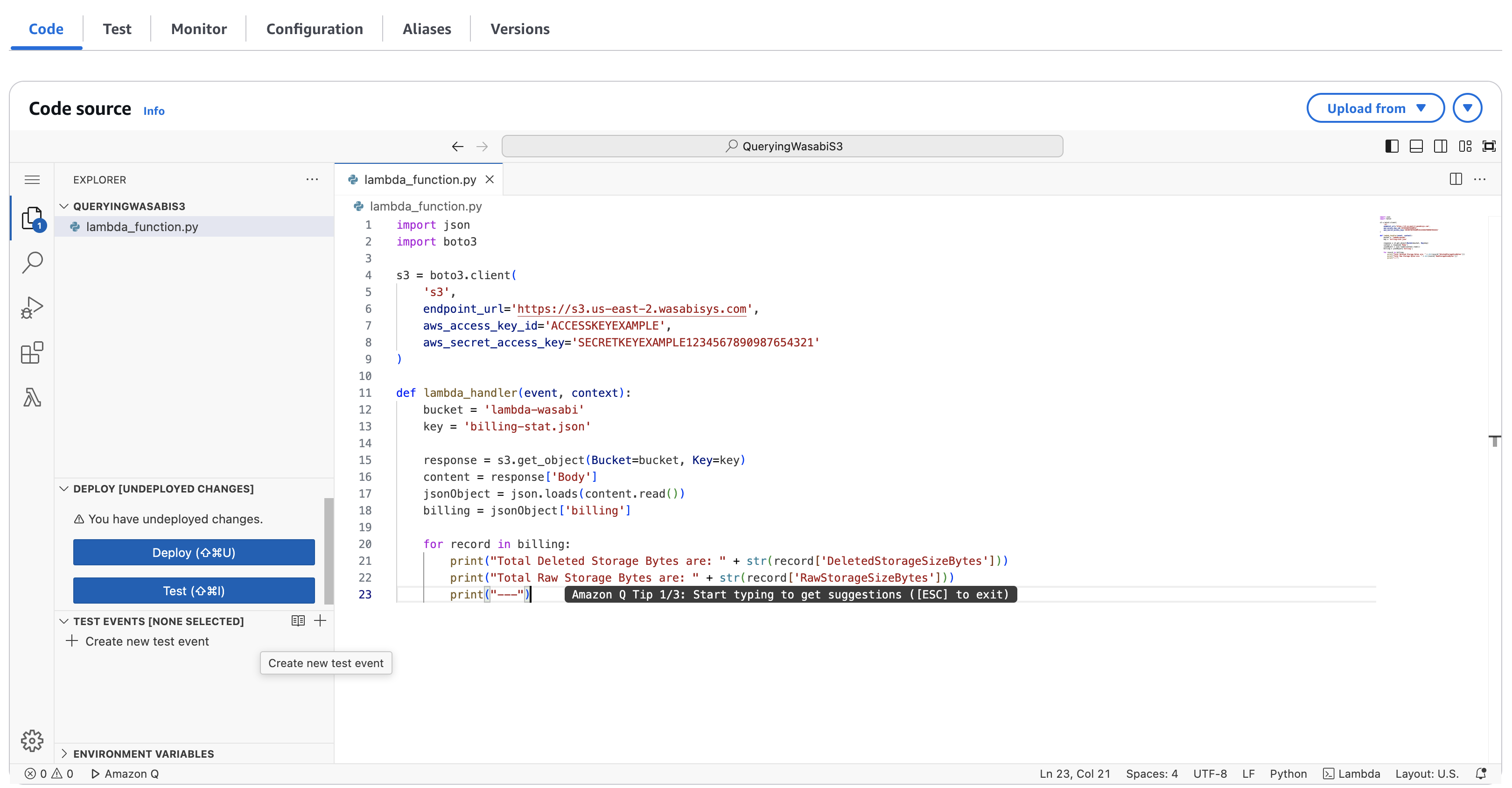
Actual code to test:
Note that this code example discusses the use of Wasabi's us-east-2 storage region. To use other Wasabi storage regions, please use the appropriate Wasabi service URL as described here
import json import boto3 s3 = boto3.client('s3', endpoint_url='https://s3.us-east-2.wasabisys.com', aws_access_key_id='Wasabi-Access-Key', aws_secret_access_key='Wasabi-Secret-Access-Key') def lambda_handler(event, context): bucket = 'Wasabi-Bucket-Name' key = 'file-name' response = s3.get_object(Bucket=bucket, Key=key) content = response['Body'] jsonObject = json.loads(content.read()) billing = jsonObject['billing'] for record in billing: print("Total Deleted Storage Bytes are: " + str(record['DeletedStorageSizeBytes'])) print("Total Raw Storage Bytes are: " + str(record['RawStorageSizeBytes'])) print("---")
Once function code is uploaded/typed/pasted, go ahead and click “Deploy” on the left-hand side to commit the code change.
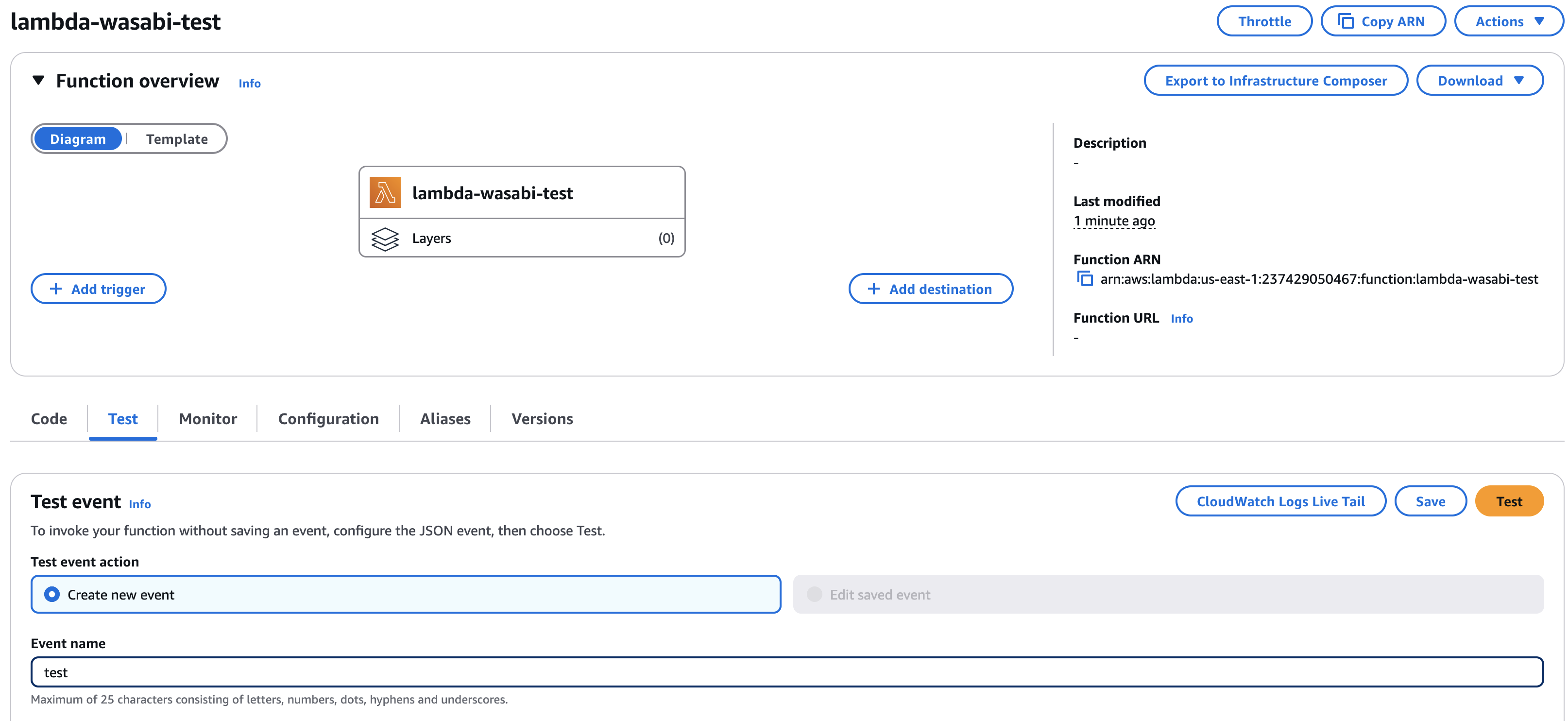
Once the code is successfully deployed, click on the “Test” tab. Give the Event a name (we are using ‘test’ for this example), and click the orange ’Test” button to execute
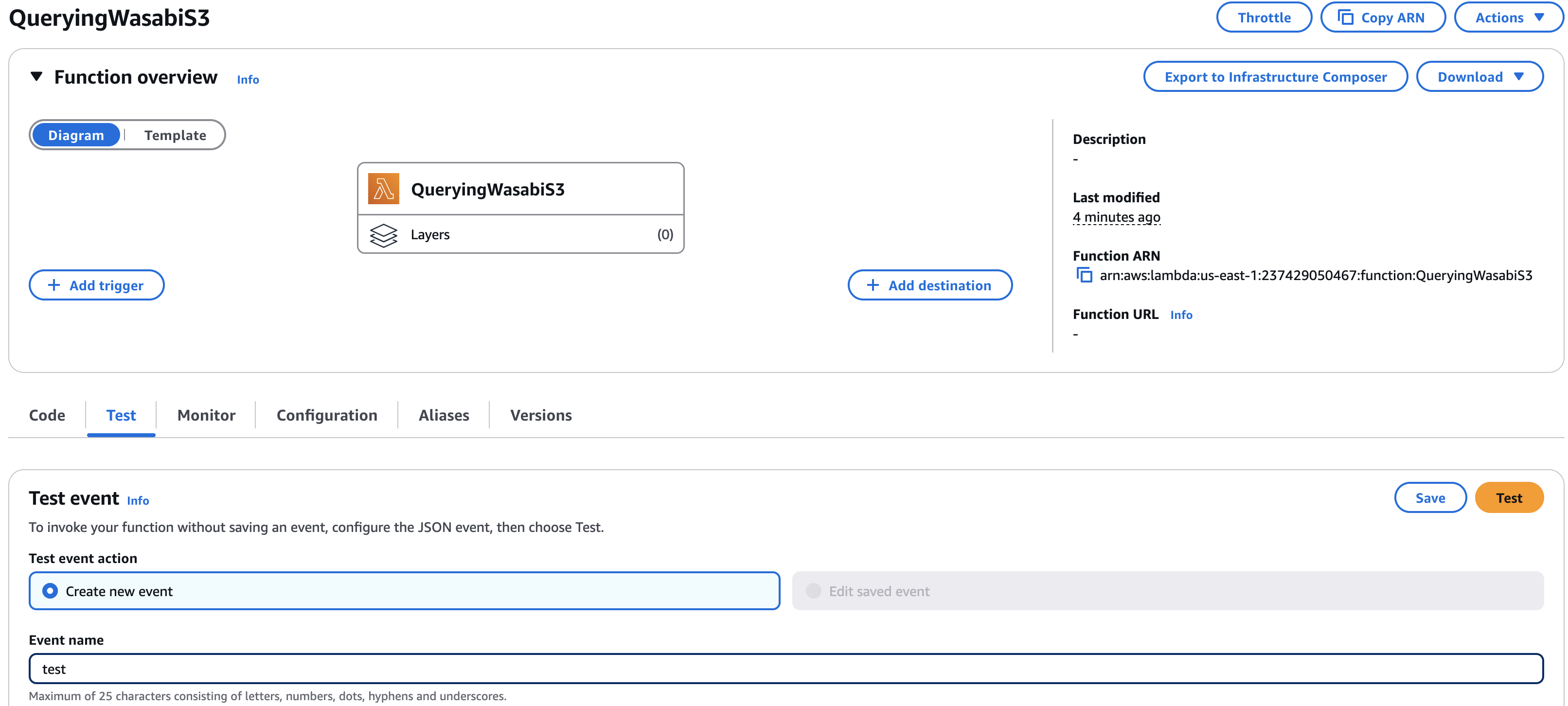
Give any Event Name and click the orange “Test” button
Below is the execution results that shows Lambda has fetched the particular data defined in the function: