How do I use Cohesity DataProtect with Wasabi?
Cohesity DataProtect is a high-performance, secure backup and recovery solution. Wasabi is validated to be used as an External Target for Cohesity DataProtect. The procedures in this article detail the steps to add a Wasabi bucket as an External Target. To learn more about the Cohesity + Wasabi solution, please refer to our solution brief.
Prerequisites
Active Wasabi Cloud Storage Account
Wasabi Bucket - See Working With Buckets and Objects
Cohesity DataProtect is installed and licensed
A VMware vCenter or another hypervisor is added as a source. A source is an object in your organization that you want to protect, such as a VM, physical server, Pure Storage volume, MS SQL Server and NAS. Refer to Register a Hypervisor Source page on Cohesity documentation for details on how to add a source or an asset for data protection. This article provides an example to protect a virtual machine on VMware vCenter, which is added as a source.
Please Note: The data restoration process is handled by your specific backup software application. As there are many potential variables that will affect your unique environment, it is strongly recommended that you seek the guidance of your backup software's technical support team in the event that you encounter difficulty, or have application-specific inquiries.
Reference Architecture Diagram

Create a Wasabi Bucket and Keys
Follow the steps in this section to create a standard Wasabi bucket. We will later use this bucket to create an External Target on Cohesity to write backups to Wasabi.
Log in to the Wasabi Console
Click on “Buckets” in the left-hand pane and then click on “Create Bucket”.
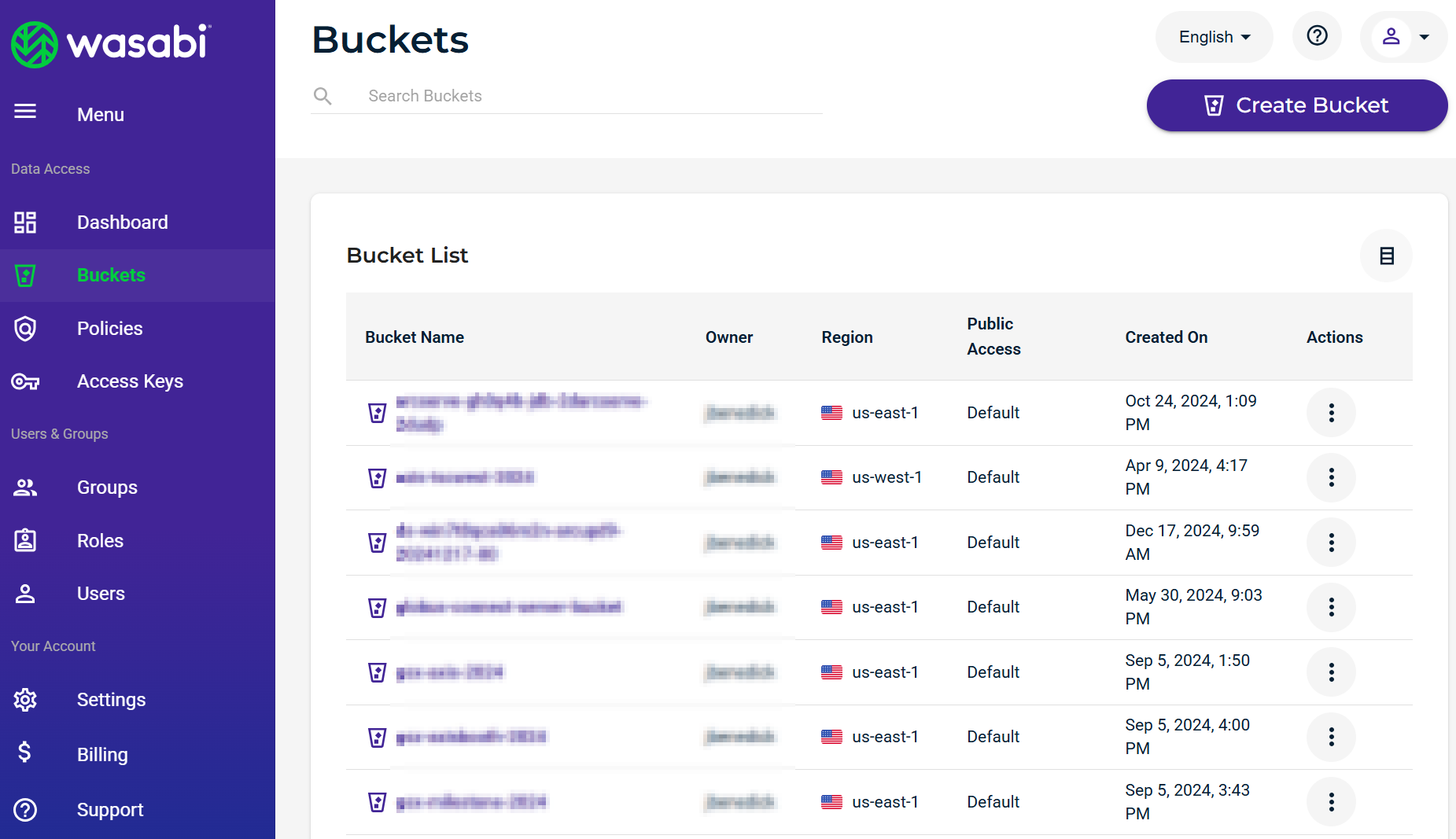
In the “Create Bucket” window, enter a unique bucket name.
Select the appropriate region and click "Create Bucket”.
Review the following Wasabi KB to create a sub-user with access keys to access the Wasabi bucket created above.
The following user permissions are required to use the Cohesity cloud services as outlined in the Cohesity Cloud Permissions section.
AbortMultipartUpload
DeleteObject
DeleteObjectVersion
GetBucketLocation
GetBucketObjectLockConfiguration
GetBucketVersioning
GetLifecycleConfiguration
GetObject
GetObjectVersion
ListBucket
ListBucketMultipartUploads
ListMultipartUploadParts
PutObject
PutObjectRetention
RestoreObject
ListBucketVersions
Adding Wasabi as an External Target
Wasabi can be added as an External Target to be used for Archival or Tiering.
Log in to your Cohesity System.
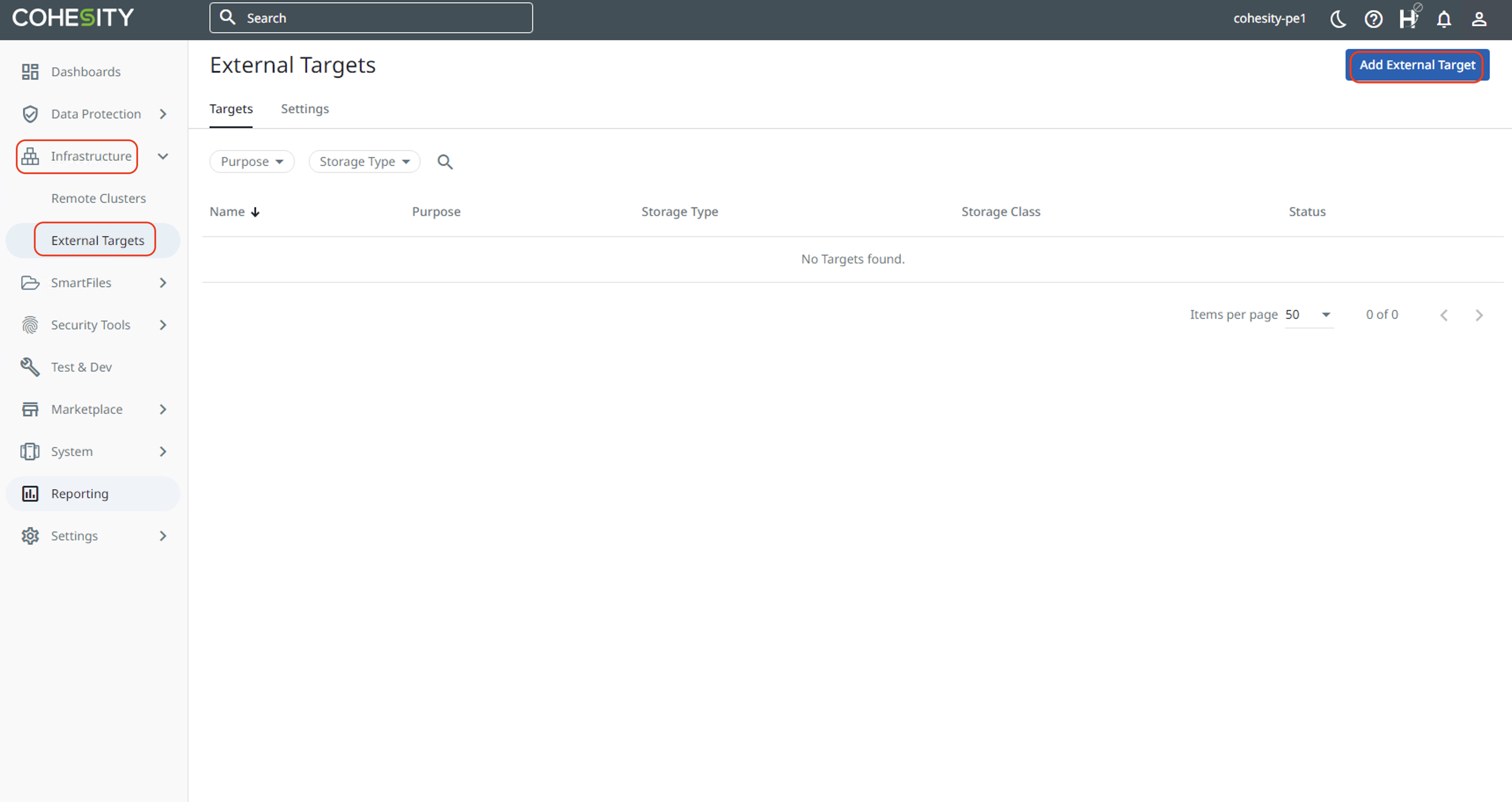
Select "Infrastructure" and then "External Targets". Click "Add External Target" on the top right.
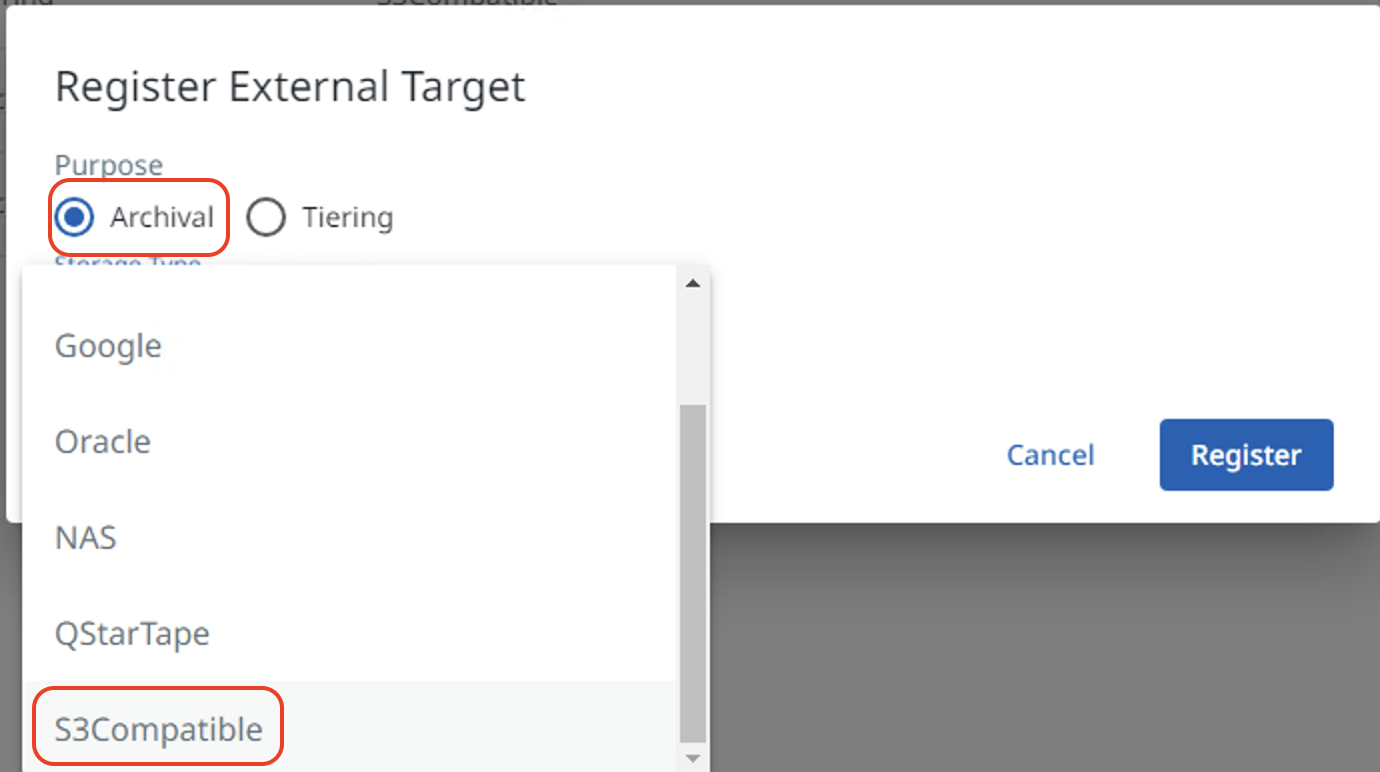
Check the "Archival" checkbox and select "S3 Compatible" from the dropdown menu.
This example uses Archival type for External Target. Cohesity has two external Target types-
Cloud Archival- Archive's benefits include long-term data retention on low-cost storage to meet compliance and retention requirements. Cohesity archive automatically copies an existing Snapshot created by Protection Groups located in a Cohesity cluster and stores it on a registered External Target.
Cloud Tier- Cohesity Cloud Tier enables an additional storage tier where cold data can be stored. You can enable Cloud Tier to move rarely used and inactive data to the cloud when HDD used capacity exceeds a set threshold.
Incremental with Periodic Full Archival Format
An archived snapshot is referred to as an archive. The first archive of a Protection Group is always a Reference Full Archive.
A Reference Full forms the basis for Incremental Archives. With incremental archives, the next archive after a reference full is an Incremental Archive. It designates the Reference Full Archive as its reference.
The Incremental Archive contains only data that is different between its reference’s snapshot and the snapshot being archived. Change blocks are computed and then changed data is compared to the reference, and the necessary data is sent to the external target. If deduplication is enabled and data did not change, only metadata is transferred.
Enter the following details-
Bucket Name - Name of the Wasabi bucket created in section 3
Access Key ID - Access key for the Wasabi user
Secret Access Key - Secret key for the Wasabi user
Endpoint - This will vary depending on your bucket’s chosen region
Port - 443
Region - Region for your Wasabi bucket
External Target Name - Name for the external target that is being added.
Archival Format - Use the default “Incremental with Periodic Full”
Once the above details are added, click "Register" to add the External target.
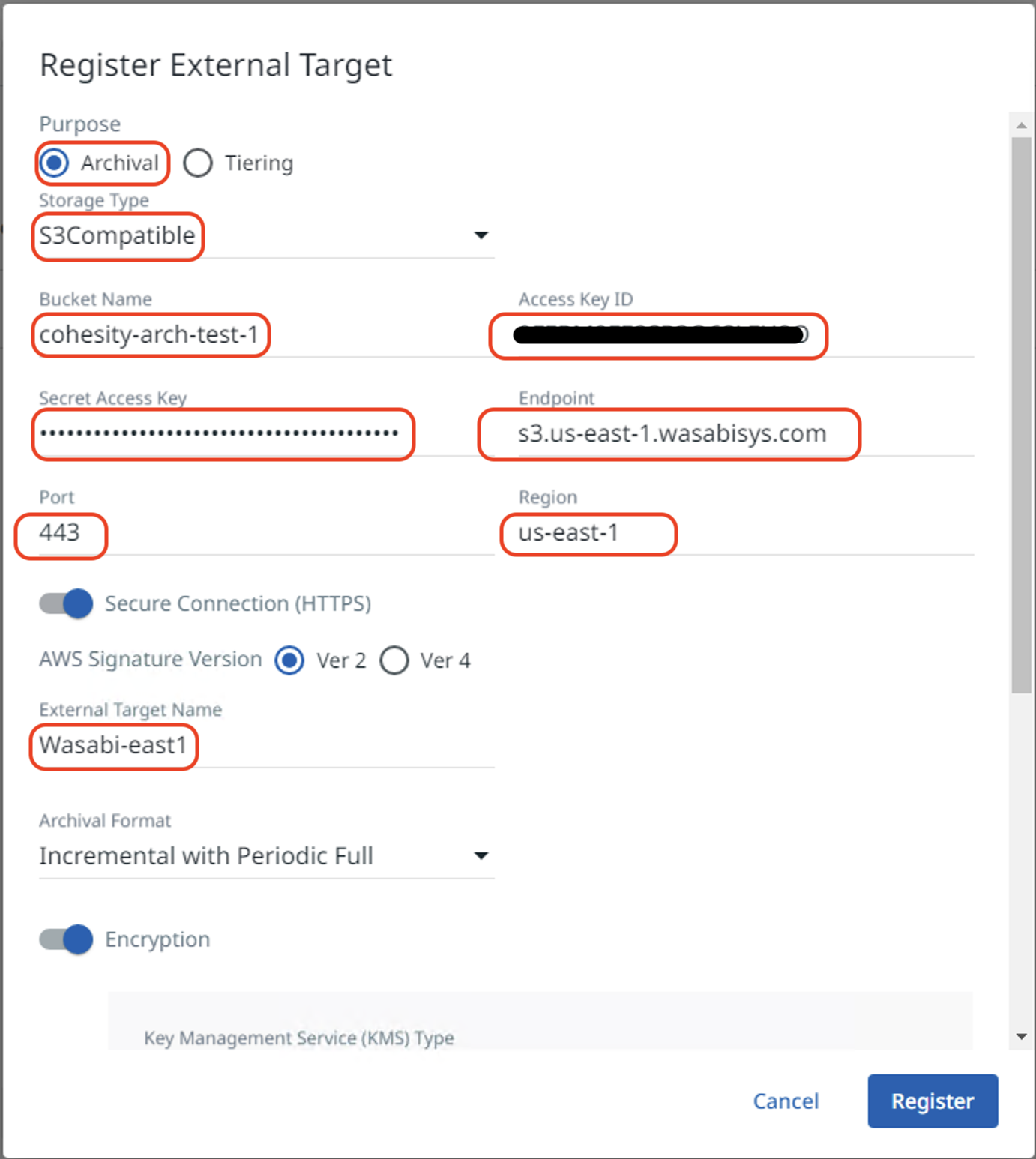
Important: This example uses Wasabi's 'us-east-1' storage region. To use other Wasabi storage regions, please use the appropriate Wasabi service URL as described in this article.
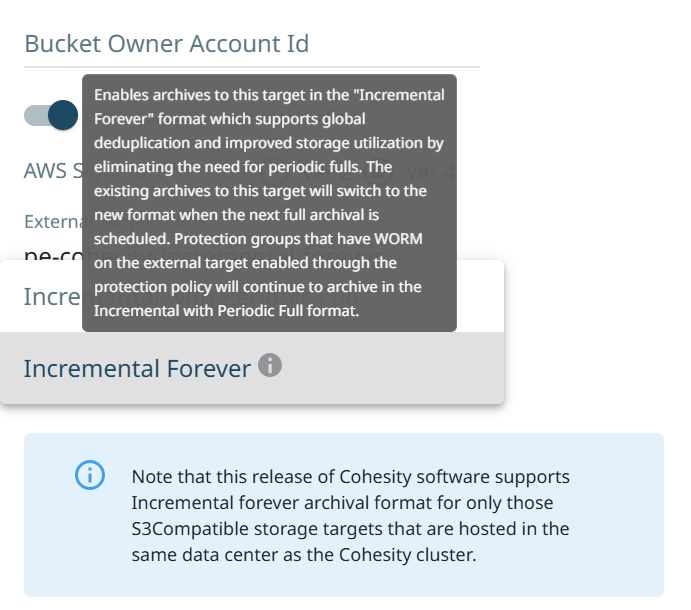
Incremental Forever Archival Format
Note: Per Cohesity Starting in 7.1.2_u2 LTS Using Incremental Forever with Wasabi is supported with caveats. With incremental forever archival format, the Cohesity cluster will download a portion of the data from the S3-compatible Standard tier external target for the space reclamation process and reupload it after compaction. This leads to increased network bandwidth usage. Before creating an Incremental Forever External Target with Wasabi Cohesity recommends having sufficient network bandwidth between the cluster and the external target. If you need help in determining if your Network speed is sufficient please reach out to Cohesity Support to consult with them about your environment.
In addition to Supporting Daily Archivals, the network should be able to additionally support daily transfer of data that will get garbage collected. This is roughly equal to Daily Change Rate (DCR) e.g. For a 1 PB Archive with 2% DCR, up to 20 TBs will be downloaded from the archive to the cluster every day and then uploaded back.
Enable this option to perform a first full archival and then incremental forever archival of data from the Cohesity cluster to an external target. Incremental forever archival eliminates the need for periodic full archive and supports global deduplication, thereby improving the storage utilization of the target.
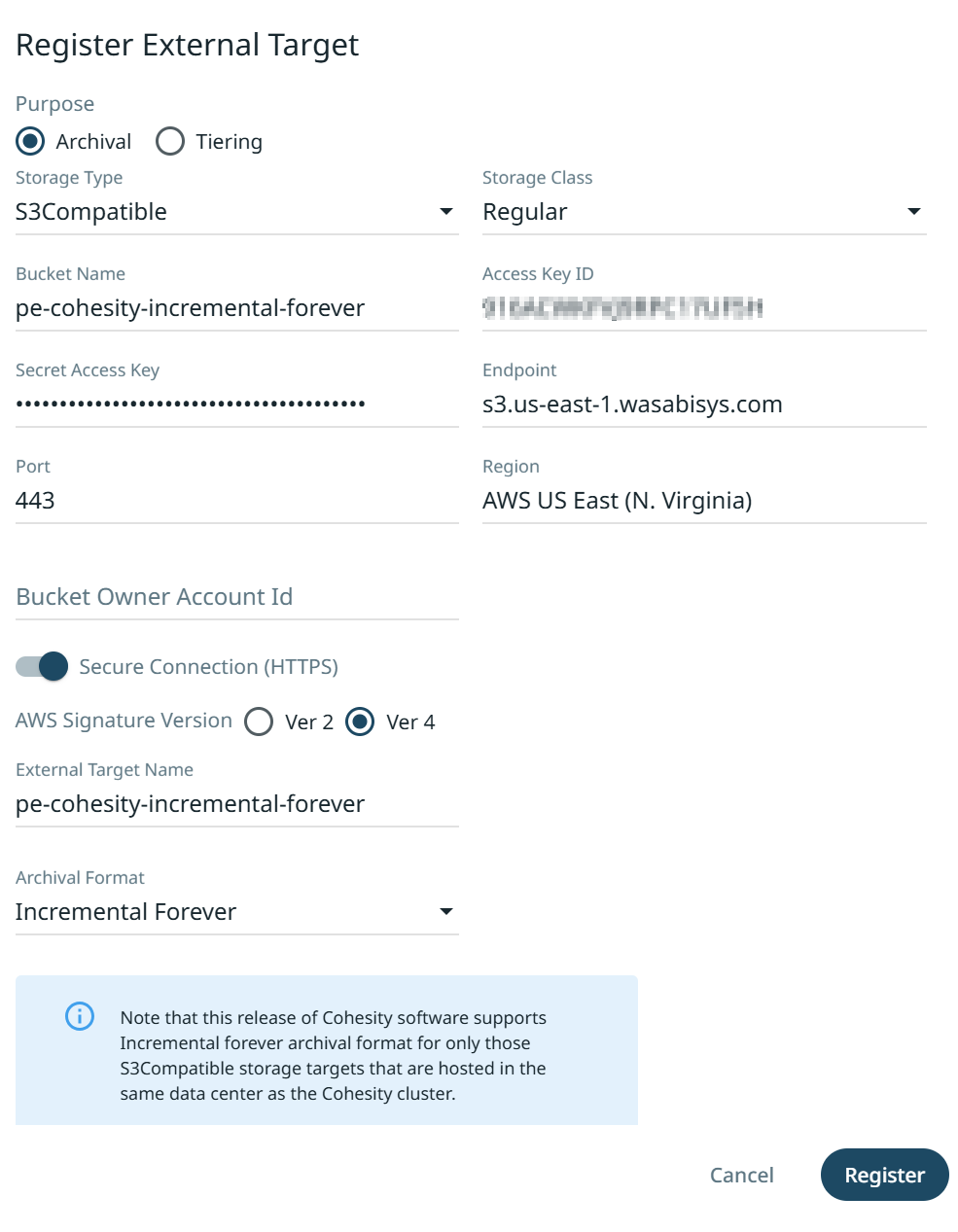
Enter the following details-
Bucket Name - Name of the Wasabi bucket created in section 3
Access Key ID - Access key for the Wasabi user
Secret Access Key - Secret key for the Wasabi user
Endpoint - This will vary depending on your bucket’s chosen region
Port - 443
Region - Region for your Wasabi bucket
External Target Name - Name for the external target that is being added.
Archival Format - Use the default “Incremental Forever”
Once the above details are added, click "Register" to add the External target.
Important: This example uses Wasabi's 'us-east-1' storage region. To use other Wasabi storage regions, please use the appropriate Wasabi service URL as described in this article.
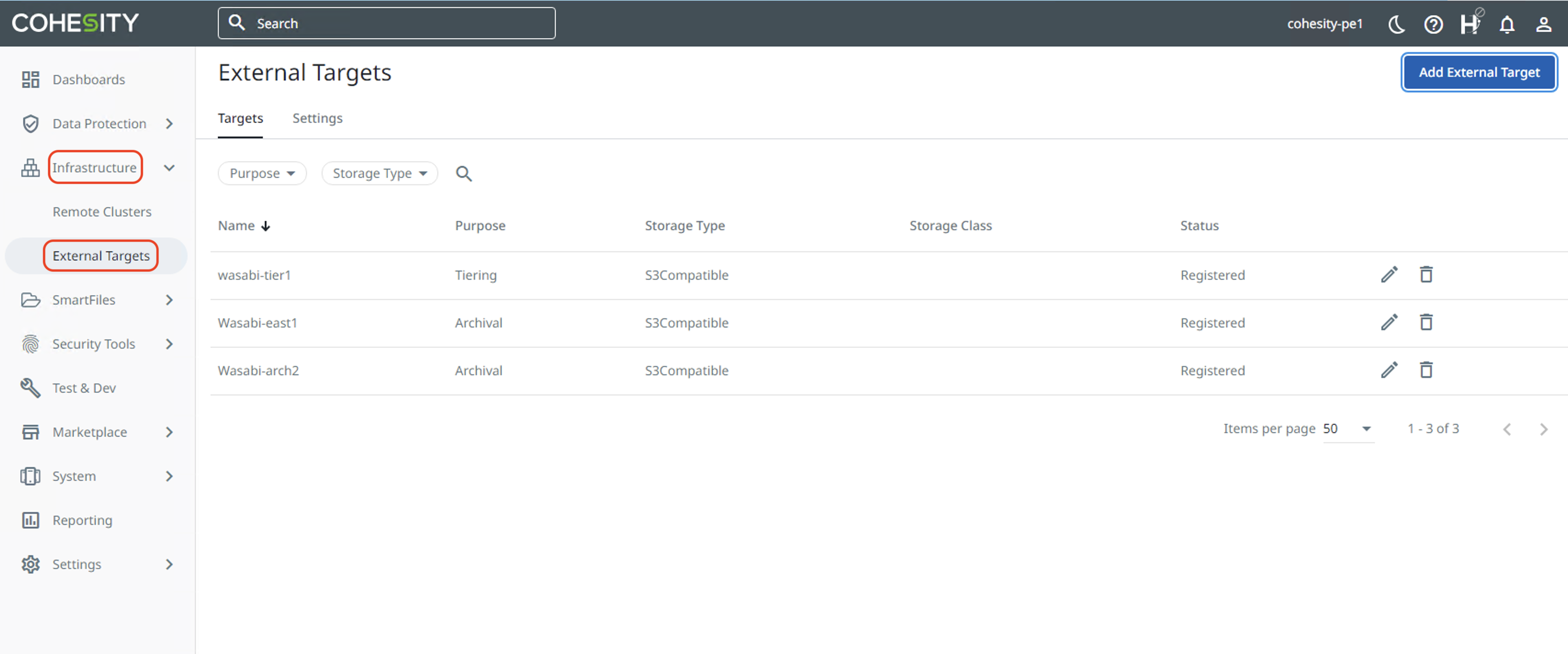
The newly created External target can be viewed by clicking on "Infrastructure" and then "External Targets".
Create a Protection Policy
A protection policy is a collection of reusable settings that define how and when sources are protected and archived. Follow the steps below to create a protection policy to archive backups to Wasabi.
Cloud Archive - Cloud Archive sends a copy of the backup data (it contains the backup data, metadata, dedupe fingerprint, and index) stored on the Cohesity Cluster to any registered external target. To perform Cloud Archive, at least one full copy of the primary data needs to be stored on the cluster.
Cloud Archive Direct - (Note: If you are running 7.1.2_u2 LTS and you created an external target with Incremental Forever Archival Format you can now archive directly to your Wasabi bucket using a CAD policy.) Cloud Archive Direct copies the data from any NAS or VMware directly to any registered external target such as Wasabi to reduce storage costs and eliminate the need to store a full backup copy on-premises.
Click on "Data Protection" and "Policies". Then click on "Create Policy".
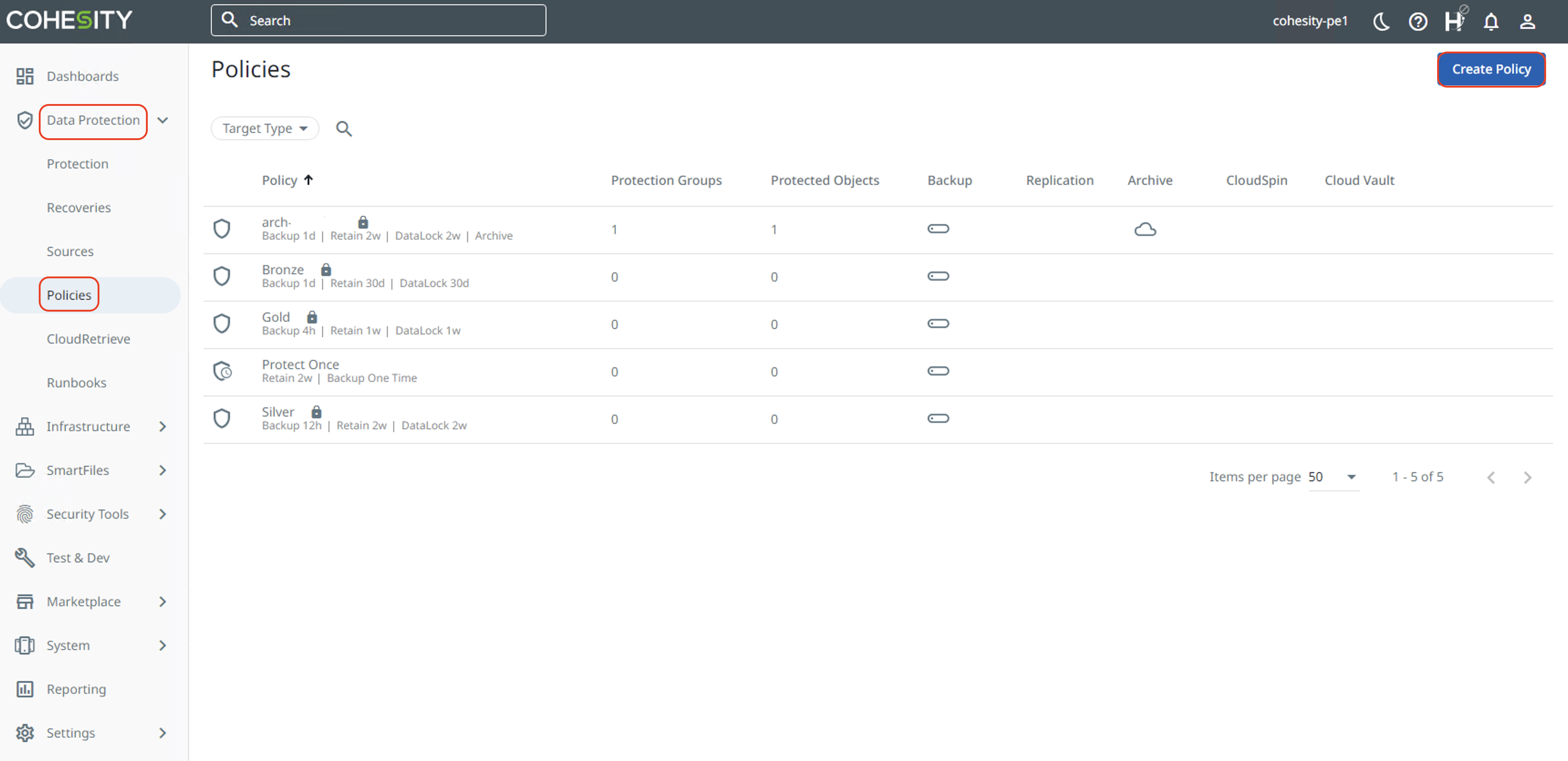
Cloud Archive Policy Creation
Input the "Policy Name" and configure the number of days/weeks to run backups and the retention period as per requirements. Click on "More Options".
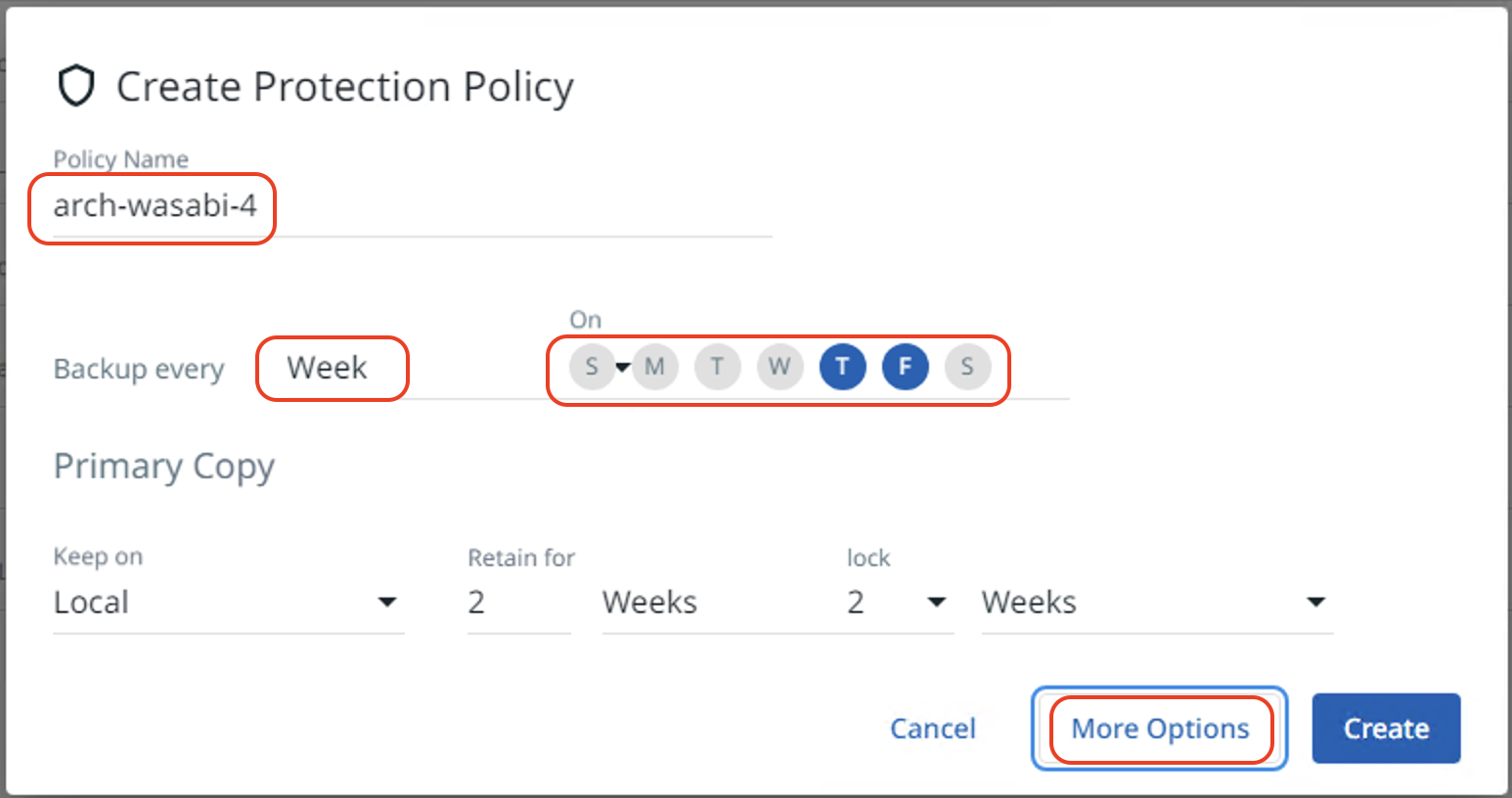
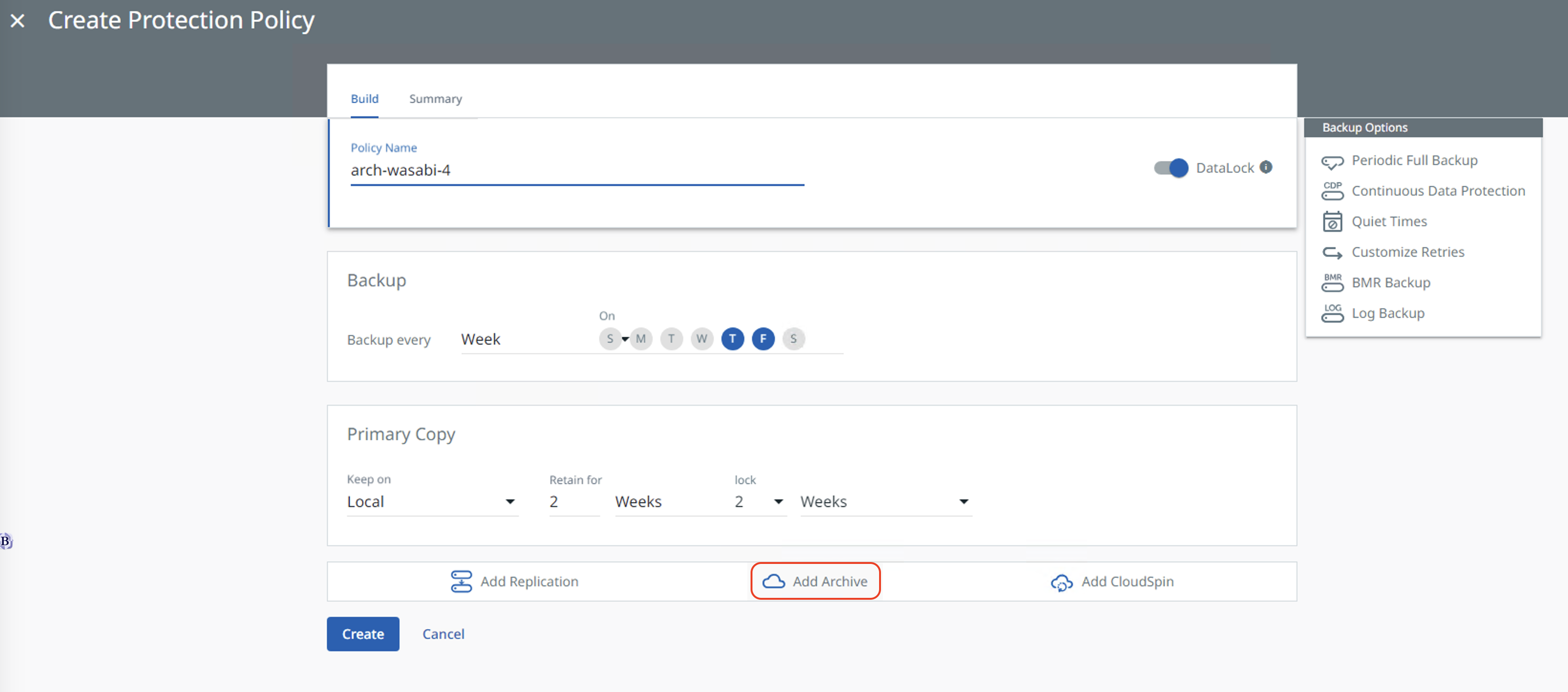
Click on "Add Archive" to add the external target pointing to Wasabi as an archive.
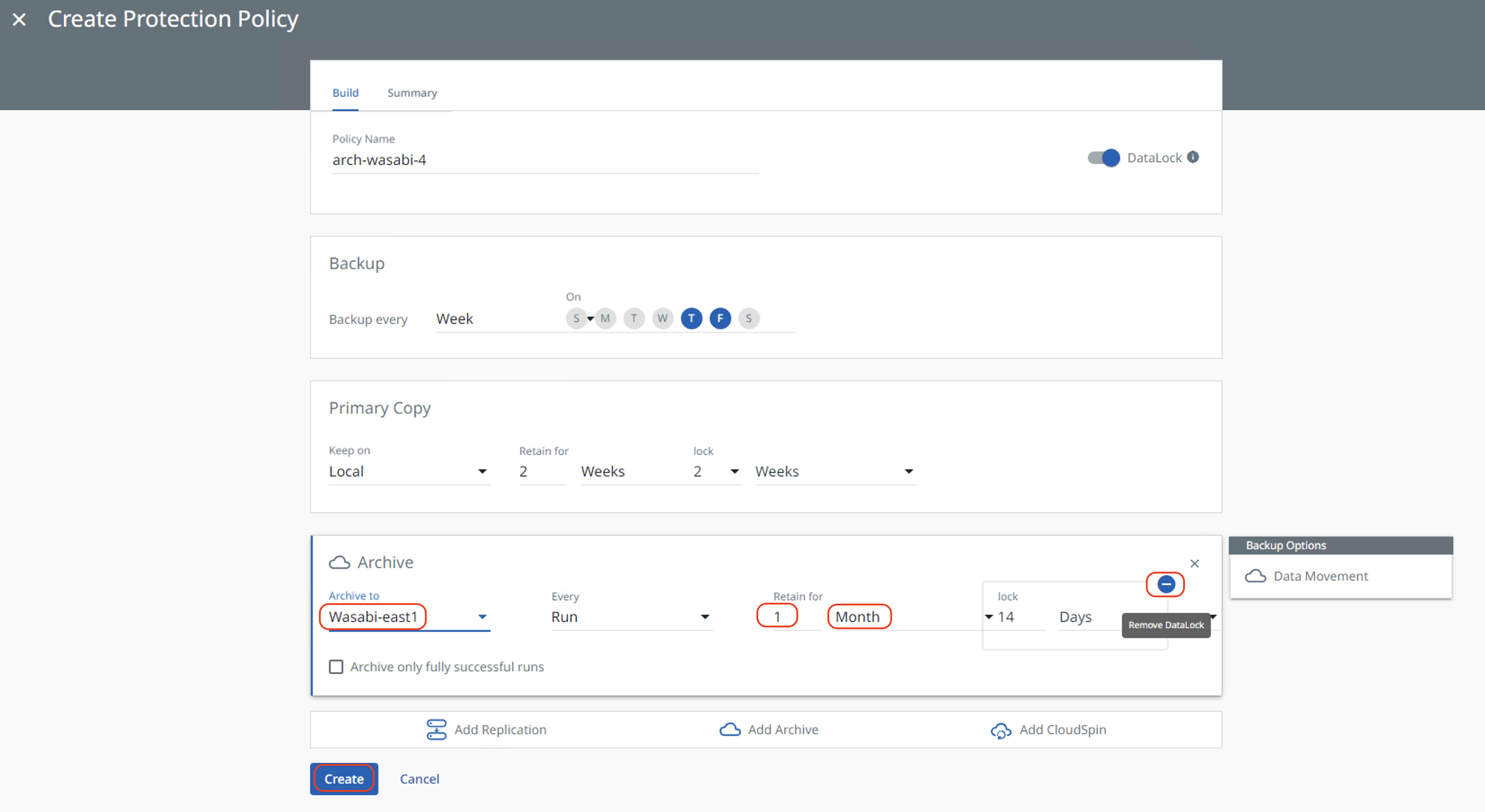
Select the Archive target that was created in Section 4 from the pull-down list under "Archive to". Configure the retention period. Remove DataLock for Archive by clicking the "-" sign beside the lock period. Then click "Create" to create the protection policy.
Cloud Archive Direct Policy Creation
Click on "Data Protection" and "Policies". Then click on "Create Policy".

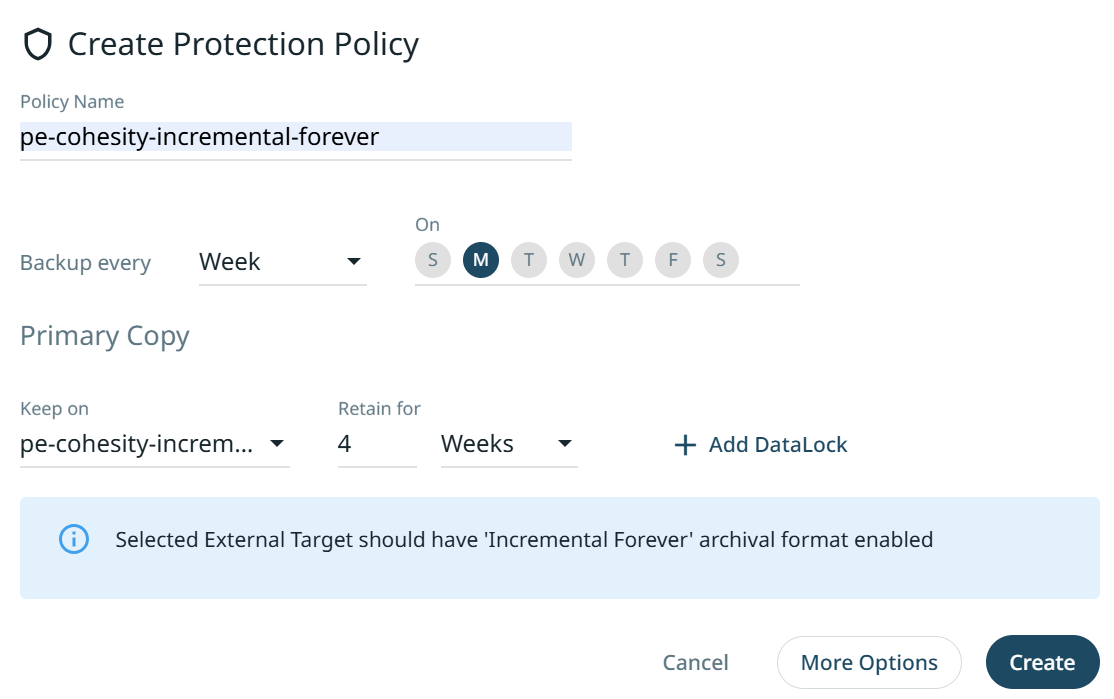
Input the "Policy Name" and configure the number of days/weeks to run backups.
Select your “Incremental Forever” Wasabi Target.
Set your retention period as per requirements.
Click on “Create”.
Create a Backup
Click on "Data Protection", then "Protection" to open the Protection page. Click on "Protect" and then "Virtual Machines".
Note: In this example, we are protecting Virtual Machines. Refer to Cohesity documentation for protecting other sources.
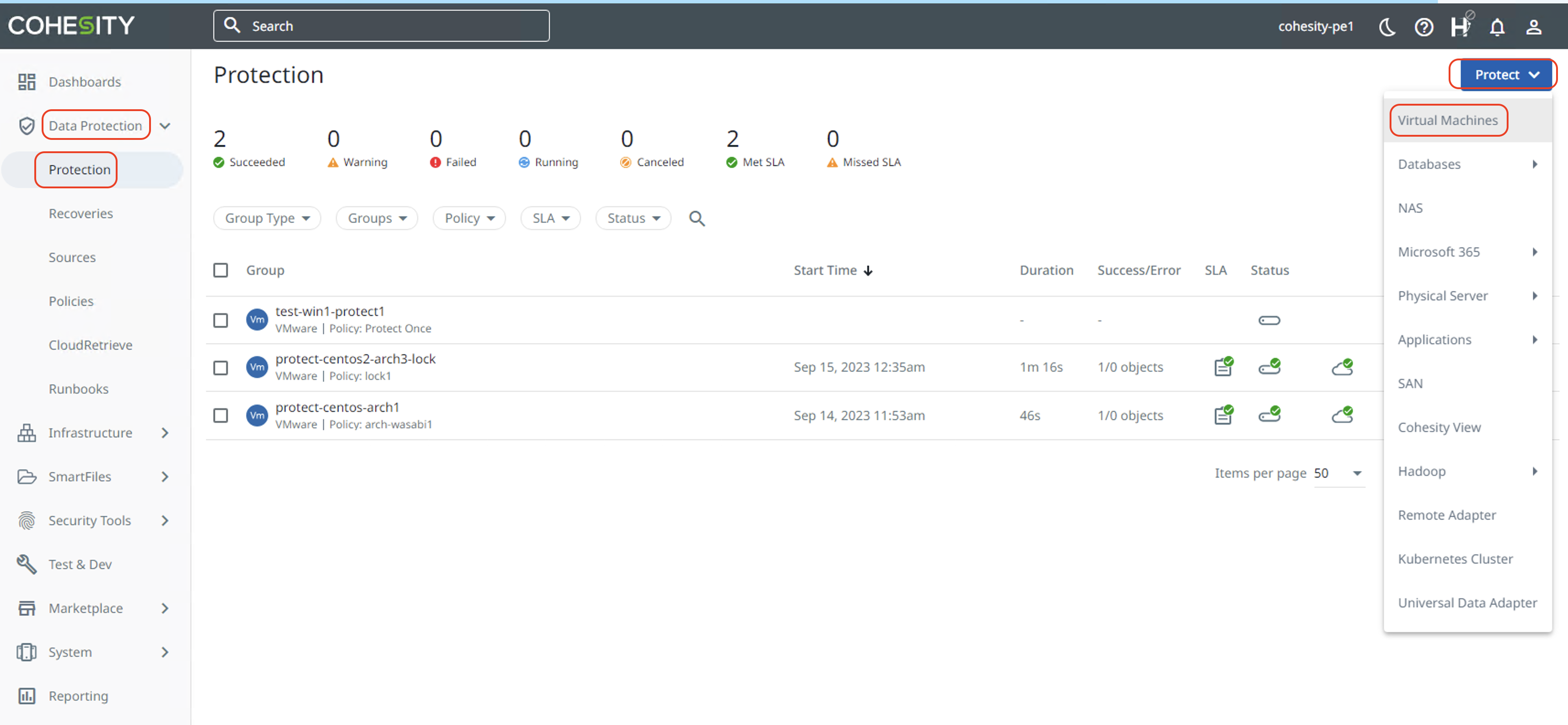
Click "Add Objects" to add the Virtual Machines for protection.
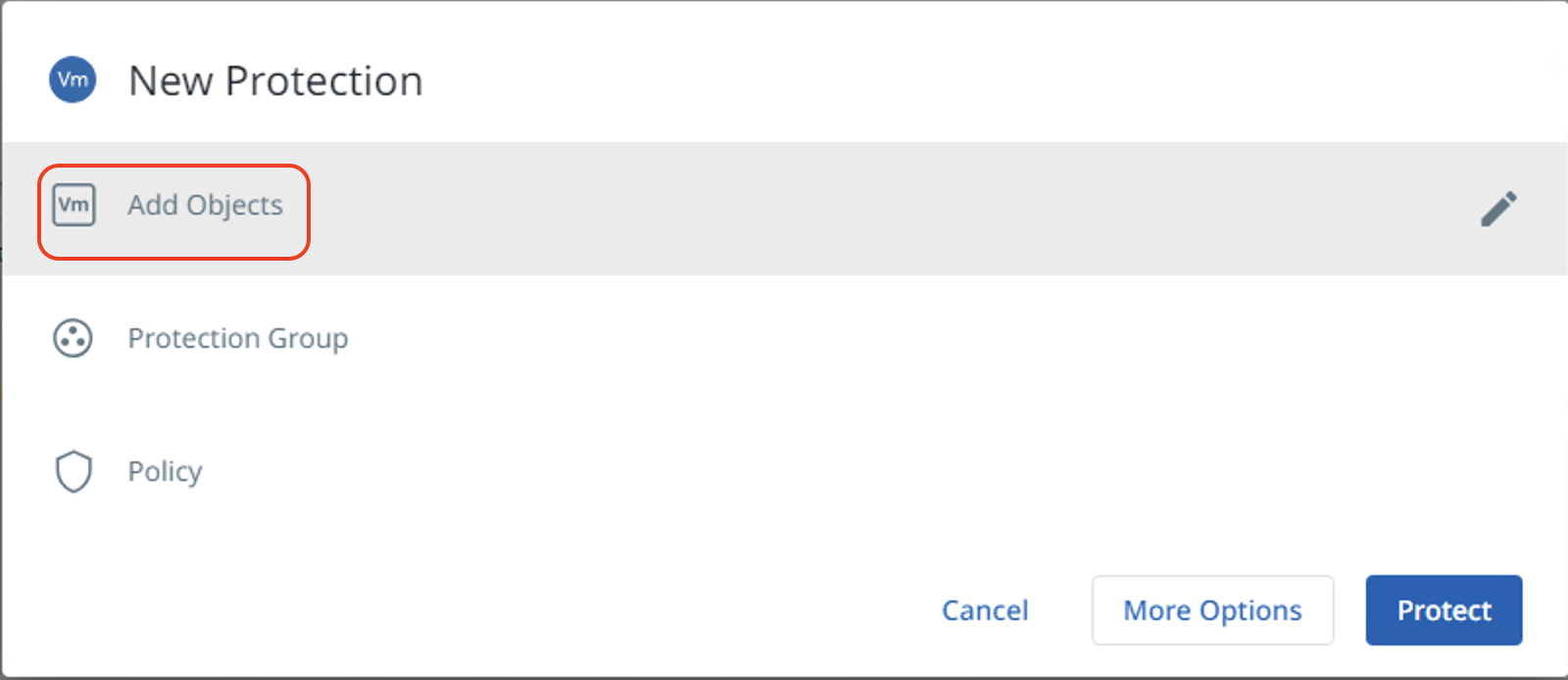
Select the Registered Source from the pull-down list and add the VMs to be protected by selecting the checkbox next to them.
Note: In this example, the source VMs are already discovered on Cohesity. Refer to Register a Hypervisor Source page on Cohesity documentation.
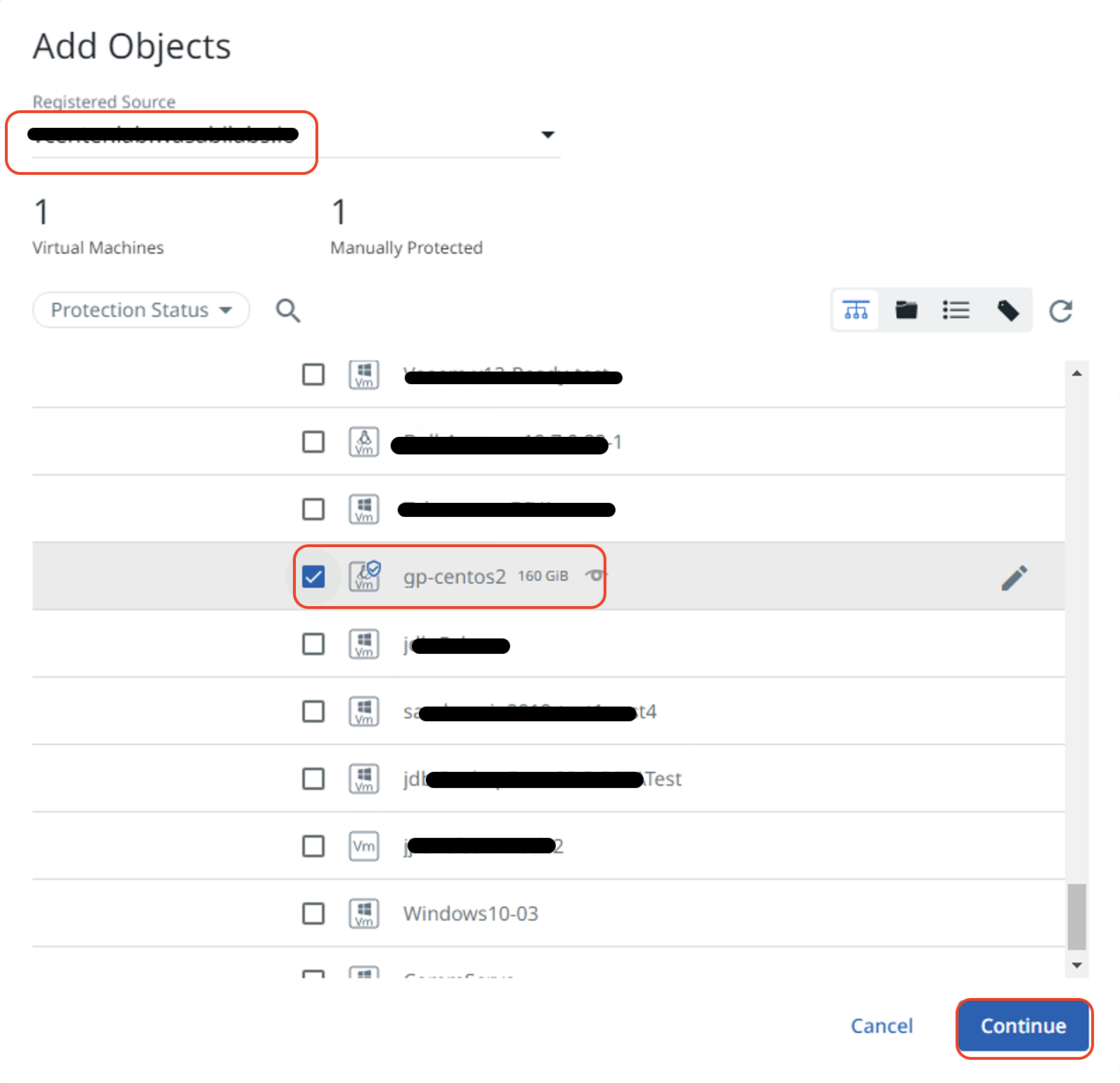
Input the name of the Protection Group if you want to create one. Then click on "Policy".
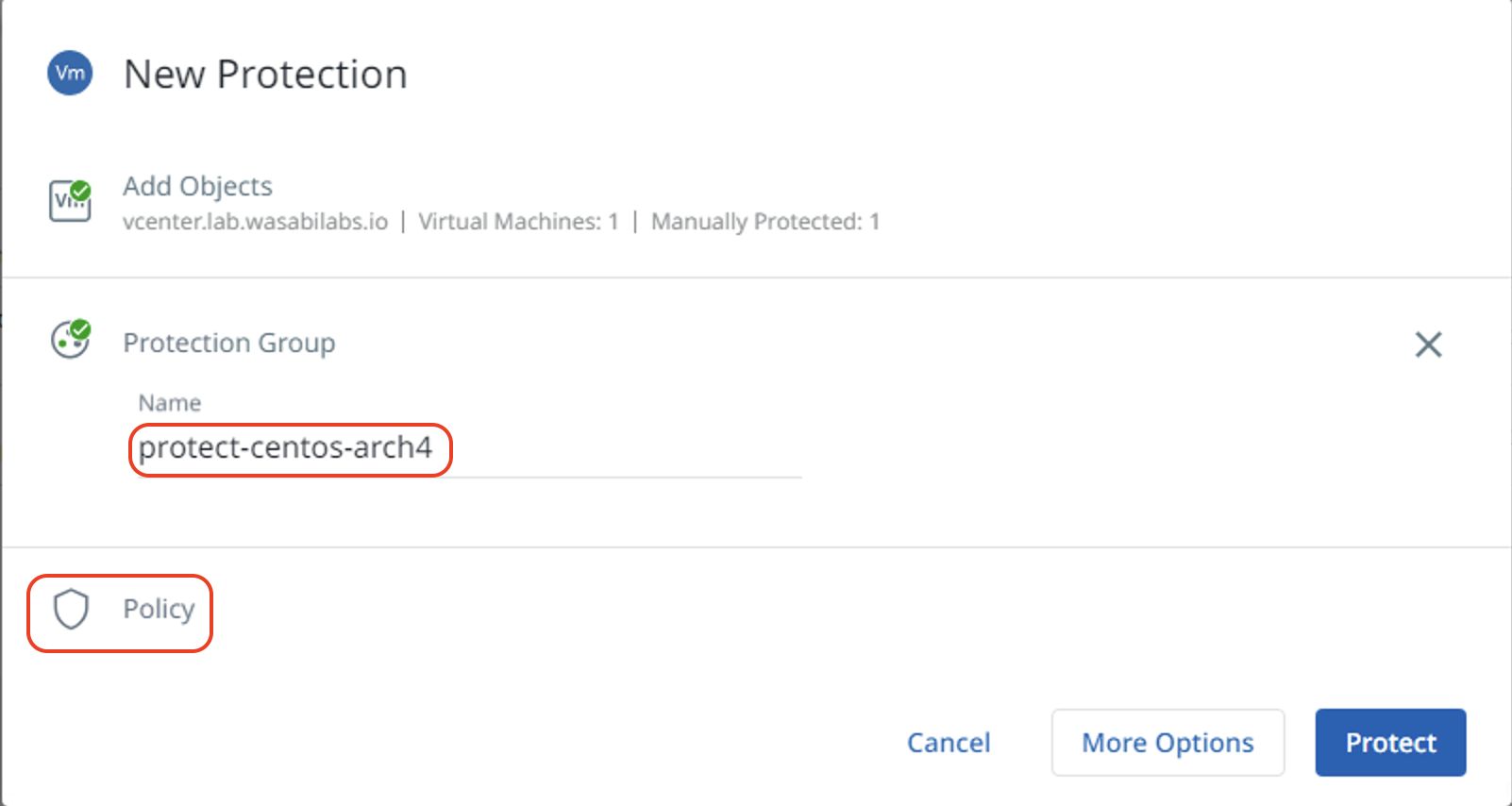
Select the protection policy created in Section 5 from the pulldown list. Then click "Protect".
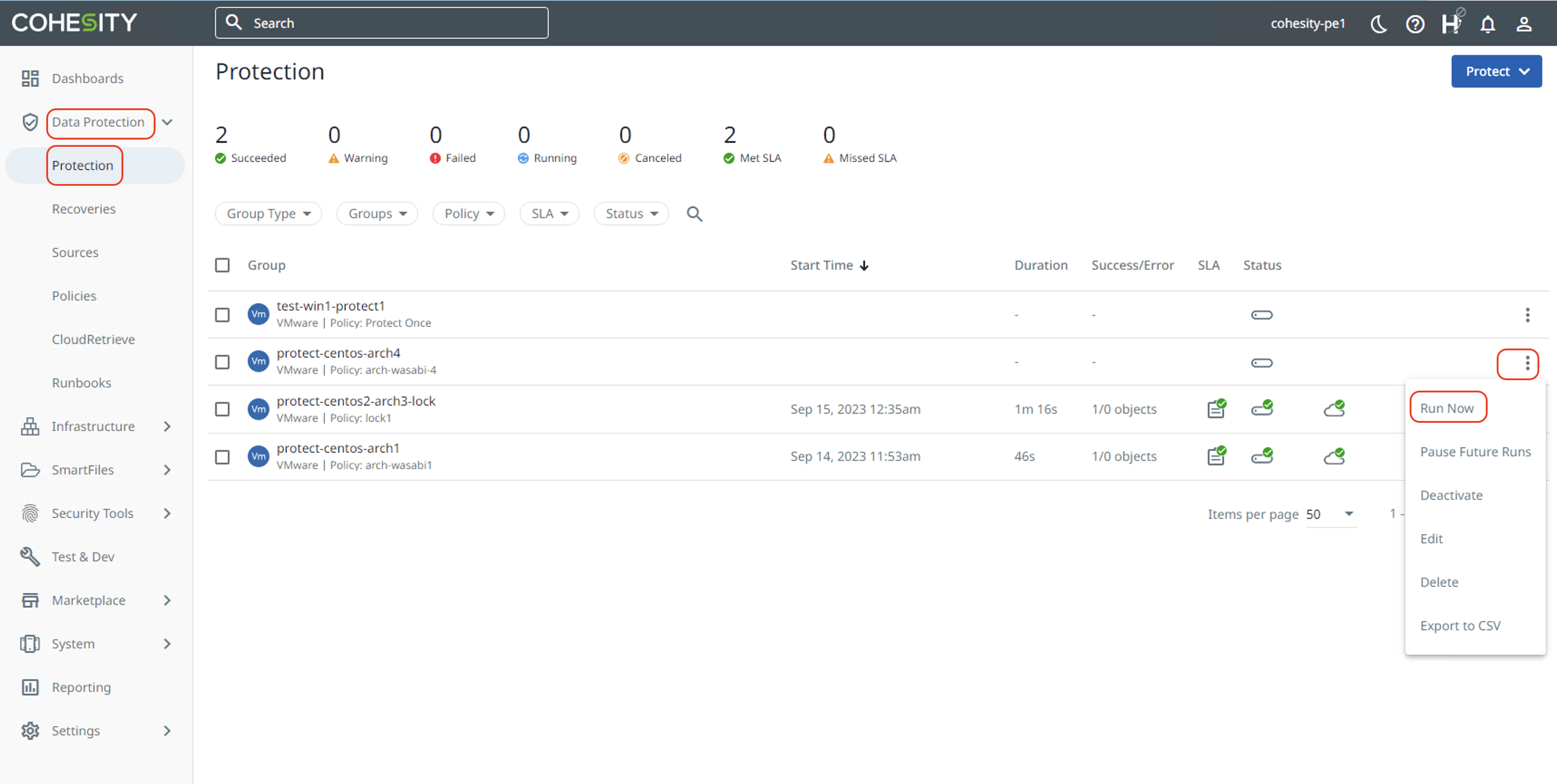
The Protection will now be added and can be viewed on the Protection page. You can run it manually by clicking on the three dots beside the protection name and clicking "Run Now".
Recovering a VM from a Backup
This example details steps to recover a VM from a backup. For recovering
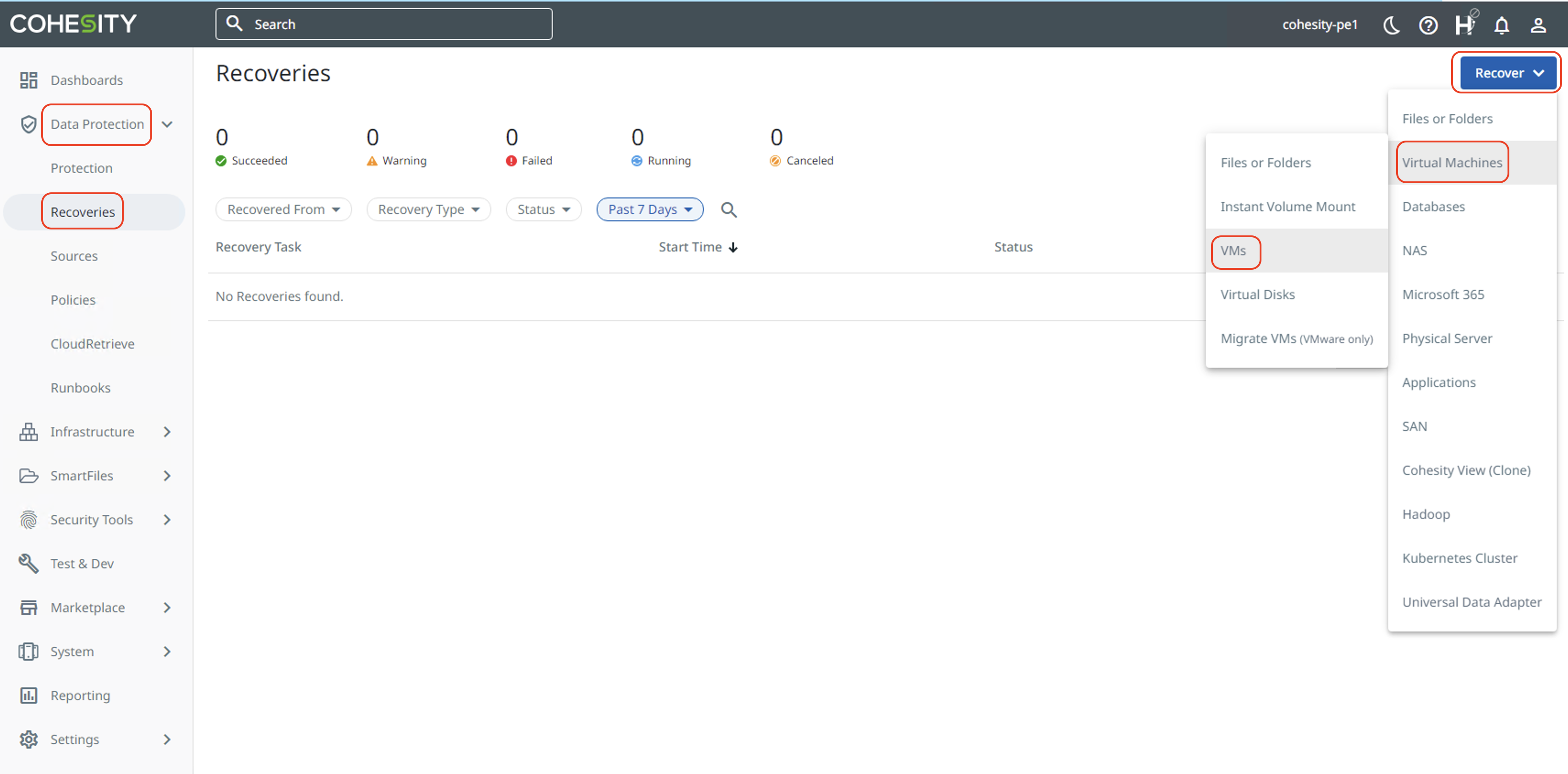
Click on "Data Protection" and then "Recoveries" to open the Recoveries page. To start recovery of VMs, click on "Recover", then click "Virtual Machines" and "VMs". To learn about other recovery types, refer to Cohesity documentation.
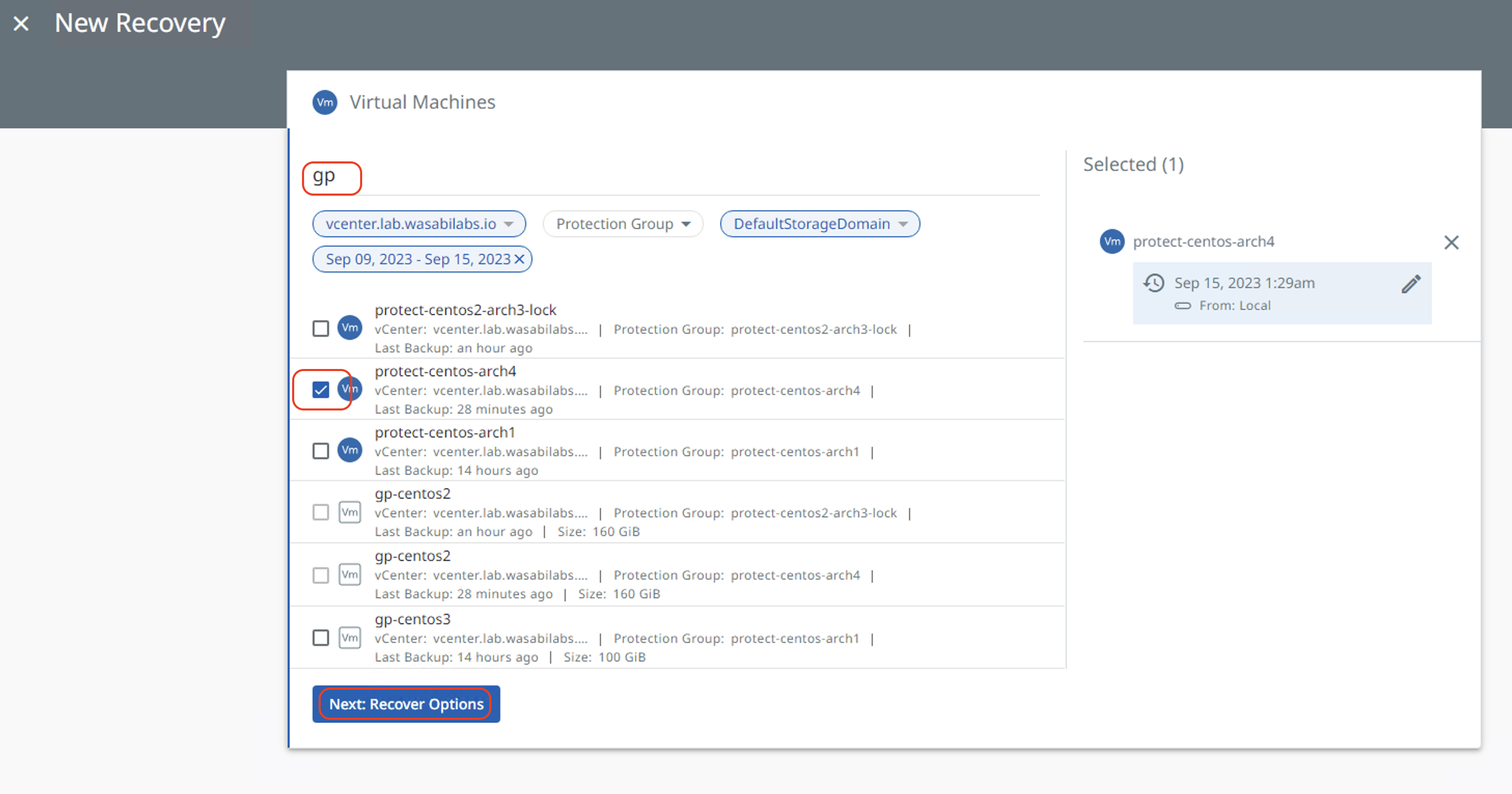
On the Virtual Machines window, search the virtual machine if you know the name or type "*" to list all VMs that are backed up. Then, select the VM you want to recover by checking the checkbox next to the VM.
Click "Next: Recover Options" to go to the next window.
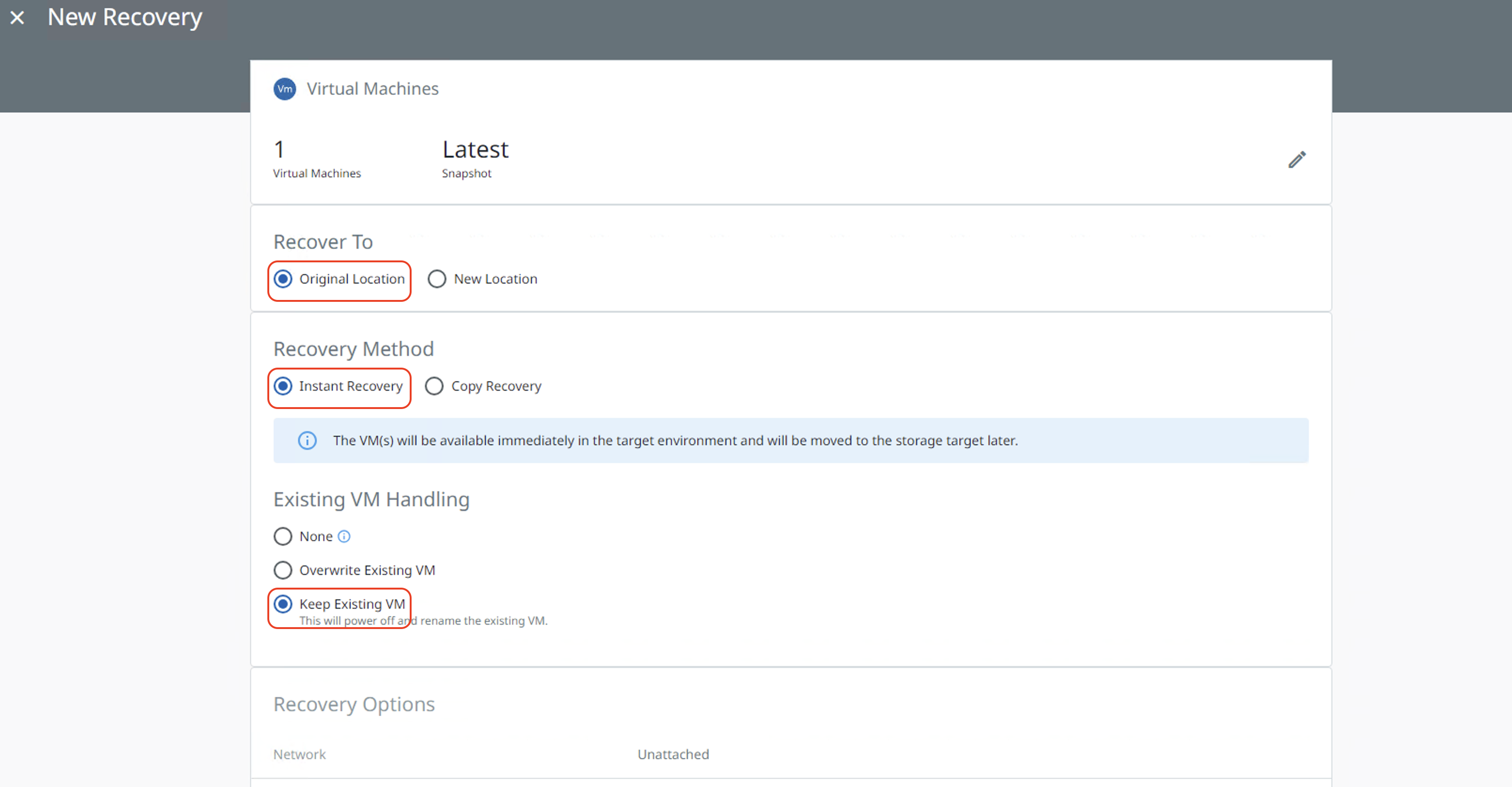
Select the Recover to location, recovery method, and Existing VM Handling option based on your requirement. Click "Recover" to start the recovery.
Recover to the Original Location—Recover the VM files (such as the VMDK files) to their original datastores and create new instances of the VMs in the original Resource Pool available in the original Source.
Recover to a New Location—Recover the VM files (such as the VMDK files) to an alternate datastore and create new instances of the VMs in an alternate Resource Pool of a registered Source.
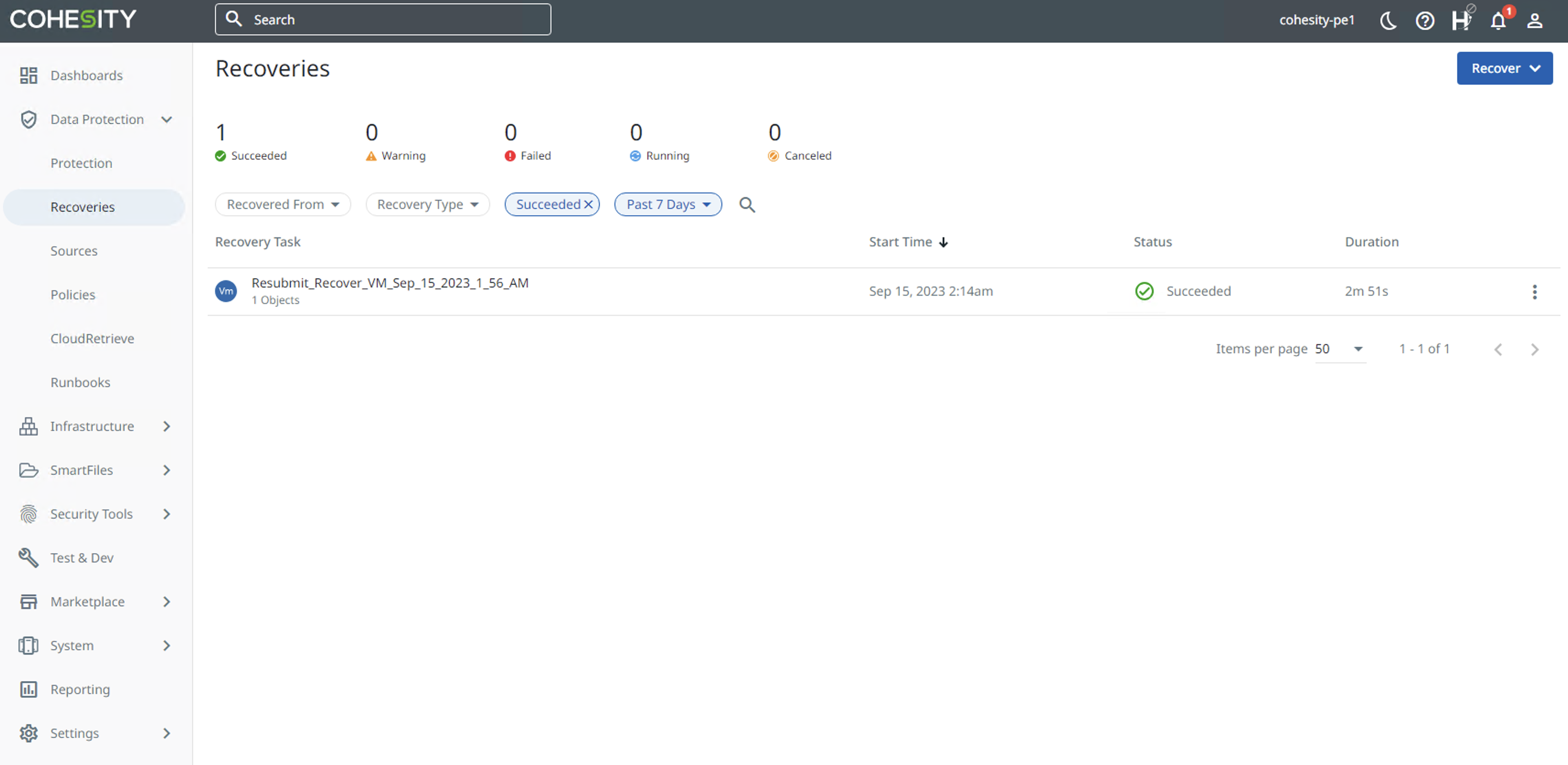
Progress of the recovery can be monitored from the Recoveries page.
Configure Immutability (Object Lock)
You can now use object lock enabled buckets with Cohesity 7.2.1.
Note: By default when creating an Archive Object Lock enabled External Target the default mode will be set to “Governance”
If you want to use Compliance mode you will need to contact Cohesity Support and open a case. They will make Cluster Config modifications to enable Compliance mode on the External Target you create.
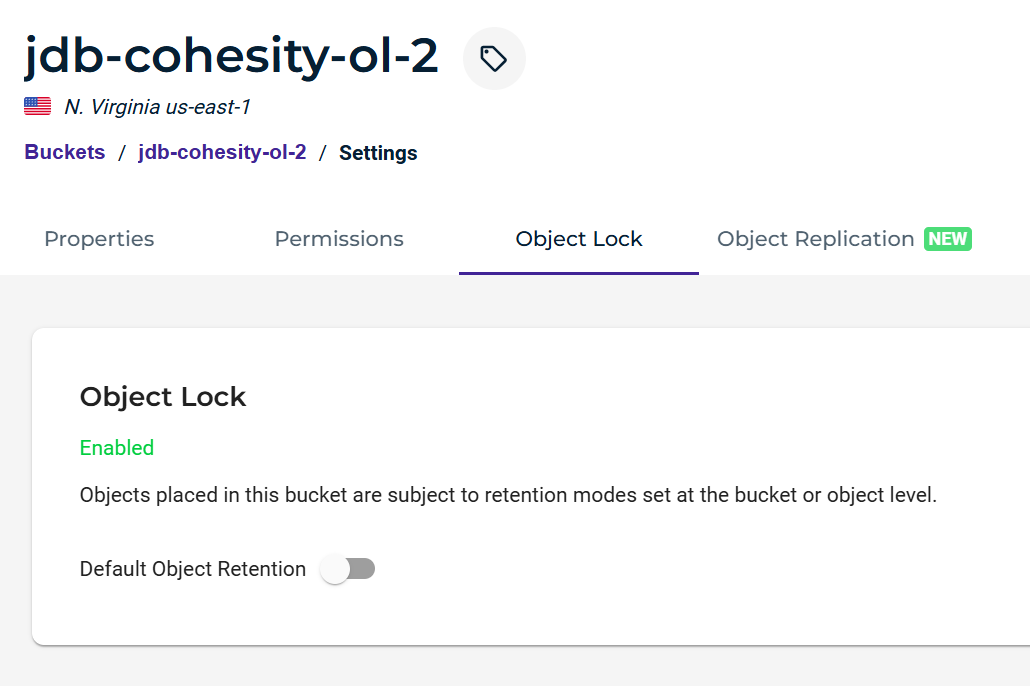
Log into your Wasabi Console and create an Object Lock enabled bucket as specified in the Object Locking KB article.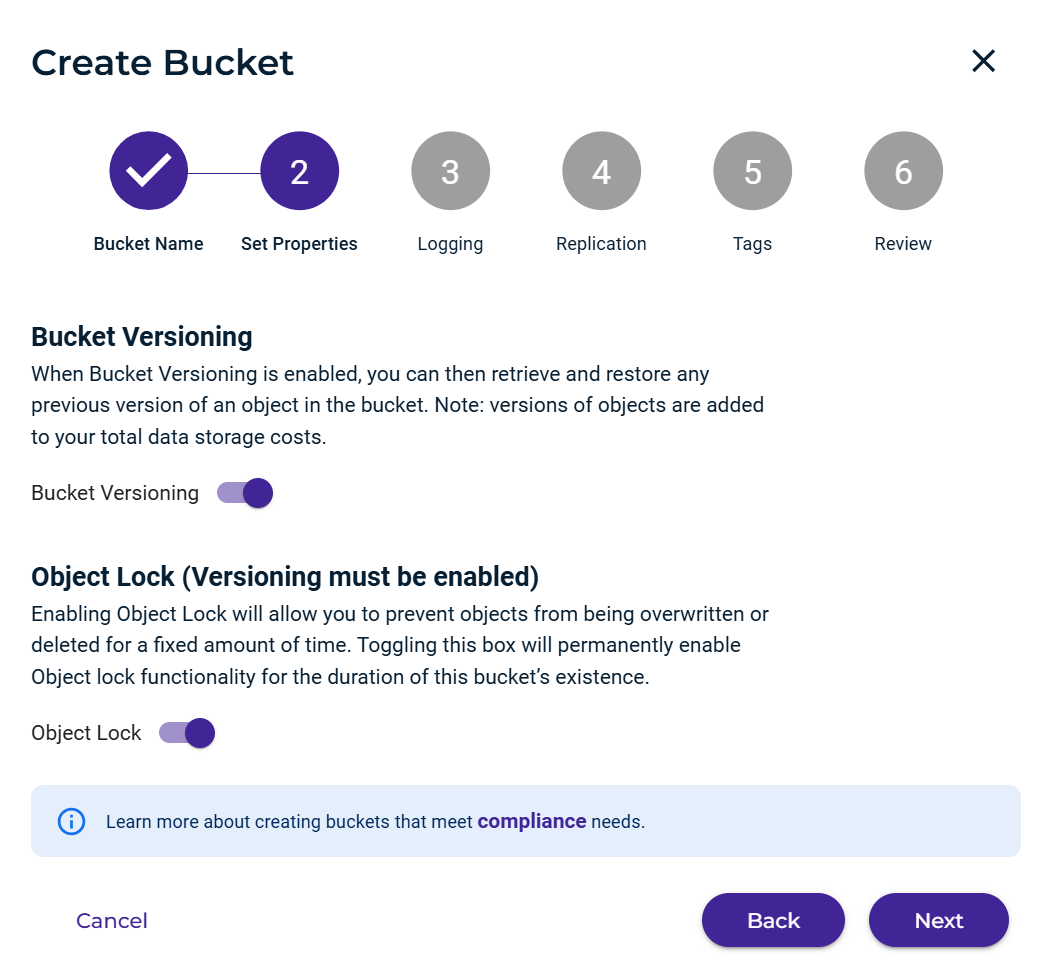
In the bucket settings, be sure not to turn on Default Object Retention, as the OL settings will be configured in Cohesity Protection Policy.
On the Cohesity web portal, click on “Infrastructure” and then click on “External Targets”.
Click on “Add External Target”.
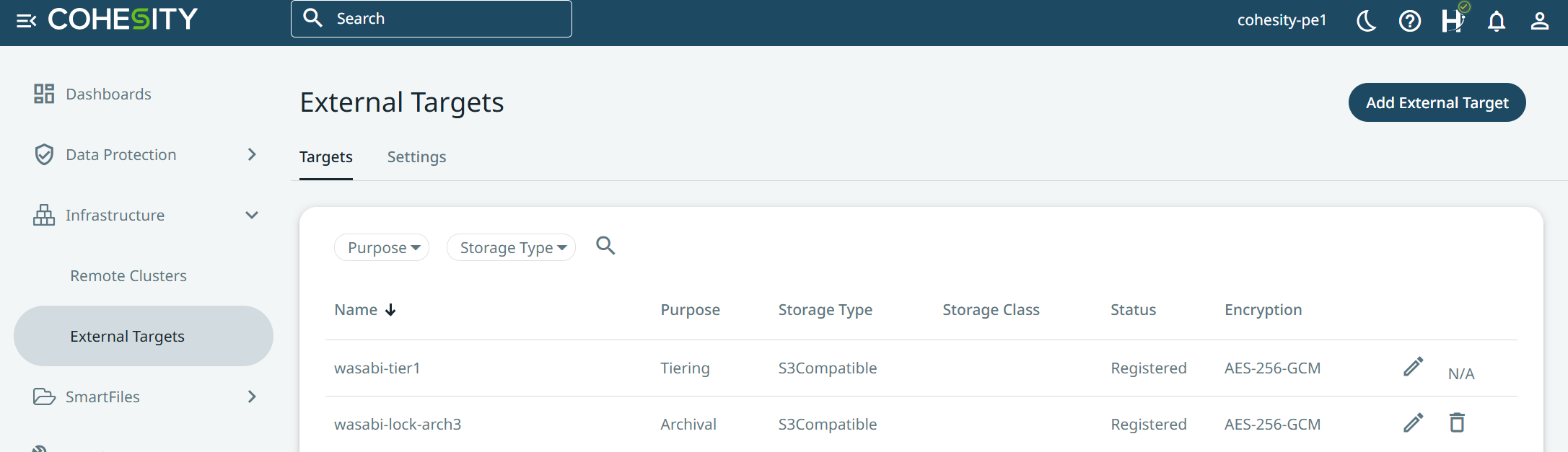
Select “Archival and then from the Storage Type drop-down menu select “S3 Compatible”.
Choose “Regular” from the Storage Class drop-down.
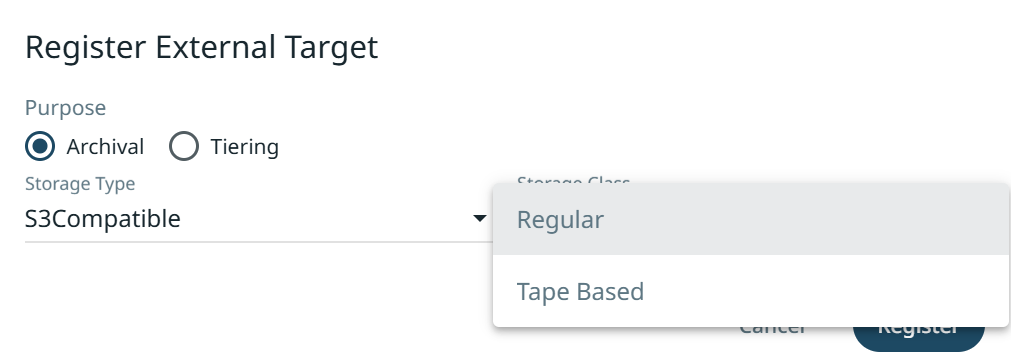
Fill in the following information:
Bucket Name - Your OL-enabled Bucket
Access Key ID - Your Wasabi Access Key
Secret Key ID - Your Wasabi Secret Key
Endpoint - The Wasabi Service URL where you created your OL bucket
Port - Port 443
Region - The matching region with your endpoint
External Target Name - Unique name for the target
Archival Format - Default will be Incremental with Periodic Full
Note: This config example discusses the use of Wasabi's us-east-2 storage region. To use other Wasabi storage regions, please use the appropriate Wasabi service URL as described in this article.
Next you can now slide the selector on for “Archive Object Lock”.

Click on “Register”.
Next, click on “Data Protection” in the left-hand pane.
Click on “Policies” and then click on “Create Policy”.
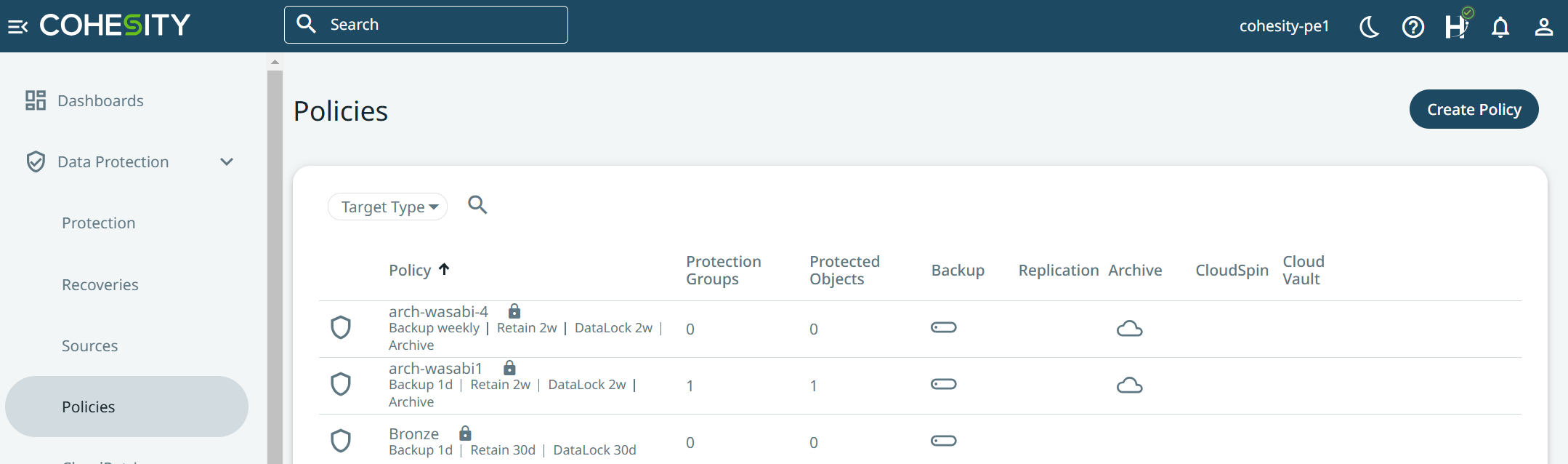
Give the Policy a unique name.
Turn off Data Lock as the Archive Target will automatically have OL settings applied.
Specify how often you want the backup to run.
Specify how long you want to keep the primary copy Locally.
Click on “Add Archive”.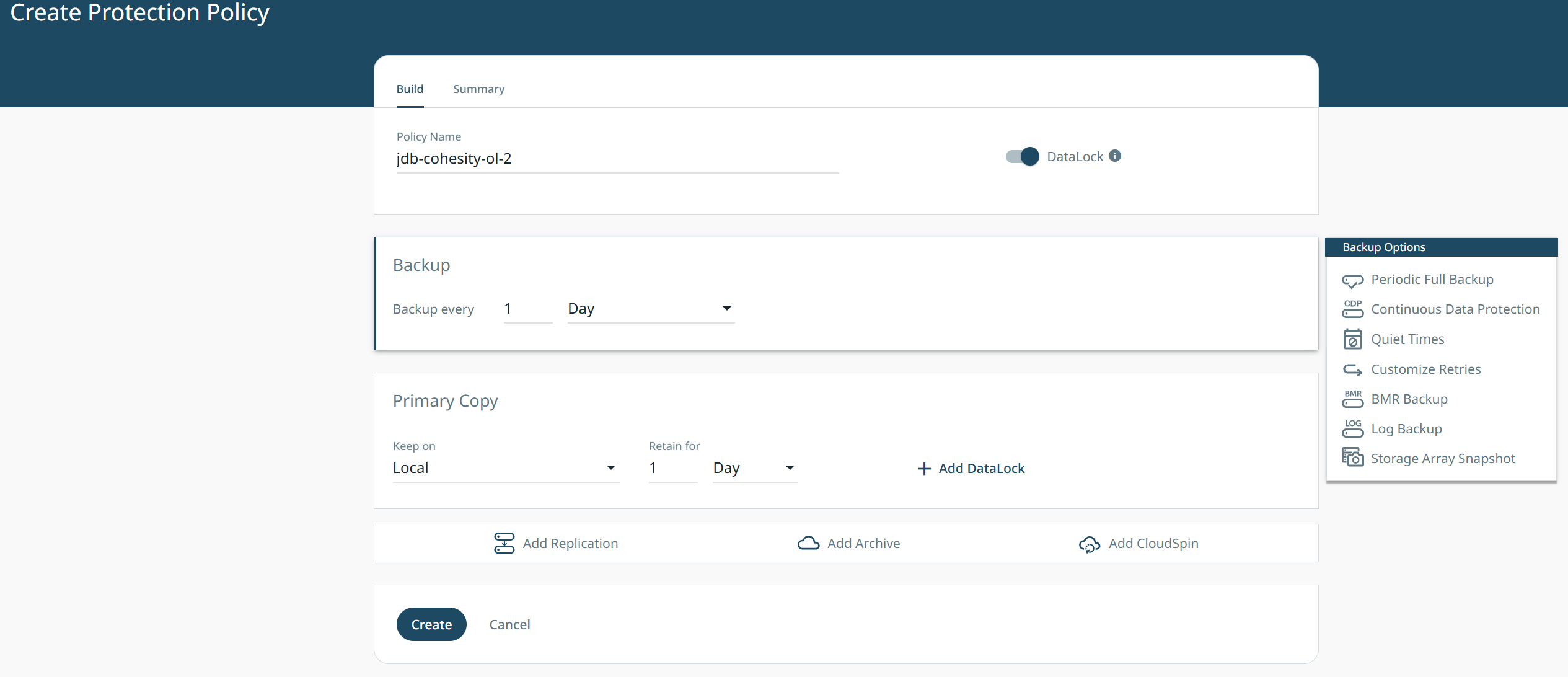
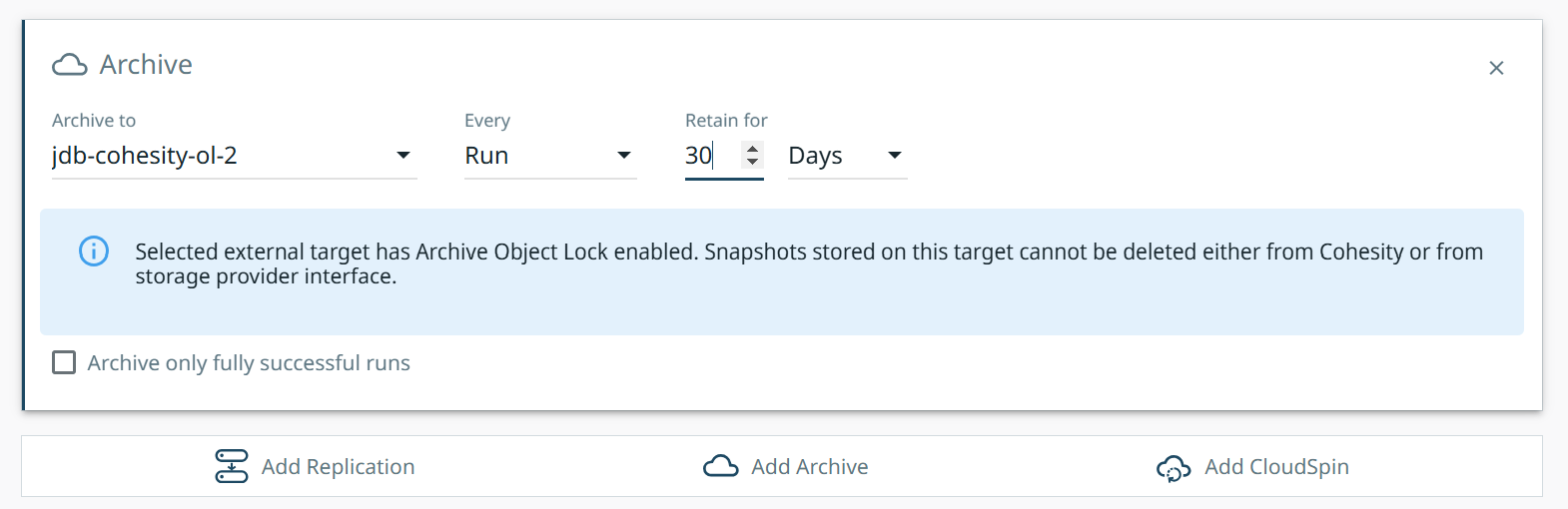
Click on the Archive To drop-down and select your OL-enabled Wasabi target.
You will now see the prompt about the External Target being Archive OL enabled. The data will be locked for as long as you specify the retention period to be and cannot be deleted until then.
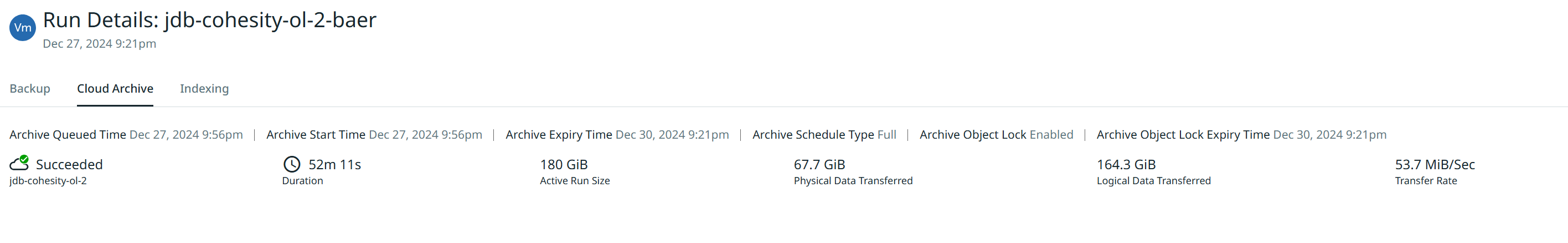
Once the backup job has run and protected the entity, you can go into the protection job and view that details. You can now see the Object Lock expiry details on when the backups will be deleted.
If you Log into your Wasabi Console and go the the data in the bucket, you will see either Governance or Compliance mode now on the data versions.