When you "virtually extend" the drive size of your Windows machine, you enable your VMS software to recognize the overall, intended storage size to meet your retention requirements. You can use this feature when your VMS software:
Does not recognize that the archived video data is being offloaded to Wasabi.
Reports that the drive is full.
This is only a virtual extension and not a real extension of storage. In reality, the volume will maintain its original size.
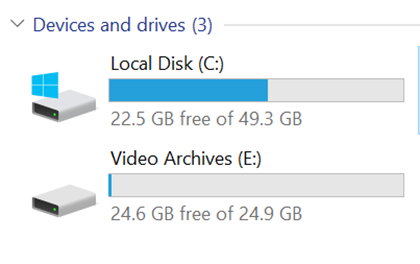
Open a Windows Explorer window and navigate to your storage drives. In the example below, notice that you can view the size of the Windows drives.
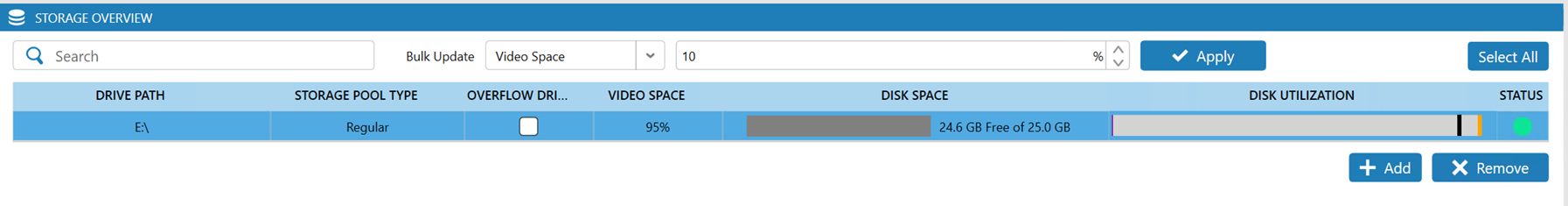
In your VMS, specify the Windows drive and location in which to use for your recording storage and the utilization of the drive. The VMS should reflect the size of the current Windows drive.
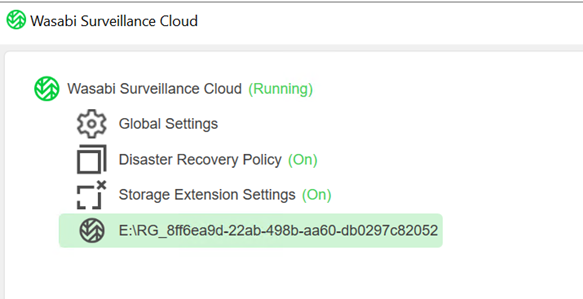
Open WSC to verify that you have WSC configured to point to the drive that your video archives are recording to. This will also affect which Windows Drive gets virtually extended to the new size that you specify in the registry key.
To create a registry key, open the Windows registry editor and enter "regedit" in either the Start Menu, Run, or CMD.
Navigate to Computer\HKEY_Local_Machine\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\tierflt.
Create a REG_DWORD.
In the Value name field, enter "VirtualExtensionSize".
Modify the newly created DWORD and enter a volume size value (in GBs) in the Value data field. In the example below, if you want to achieve 30 days of retention (with two days being on-premise and 28 days being in the cloud) specify the overall storage required for 30 days of consumption. If each day requires 1 TB of storage, specify 30,000 GBs (or 30 TBs) of virtual drive space.
Under Base, select Decimal.
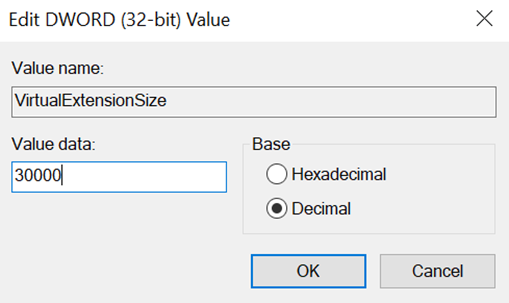
Your registry entry should look like the following highlighted entry:
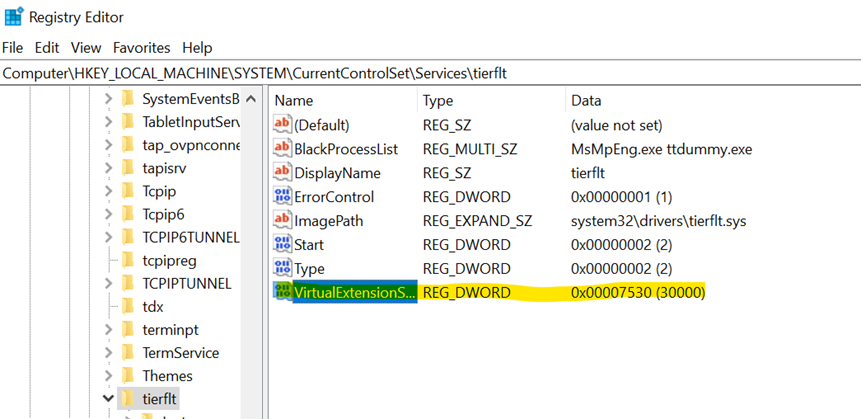
After creating the value, exit the registry editor.
Restart the machine to refresh the changes.
Optionally, restart WSC services using the command prompt.
Optionally, to avoid restarting the machine, run the following command lines into an administrative CMD:
- net stop tiersvc - net stop tierflt - net start tierflt - net start tiersvc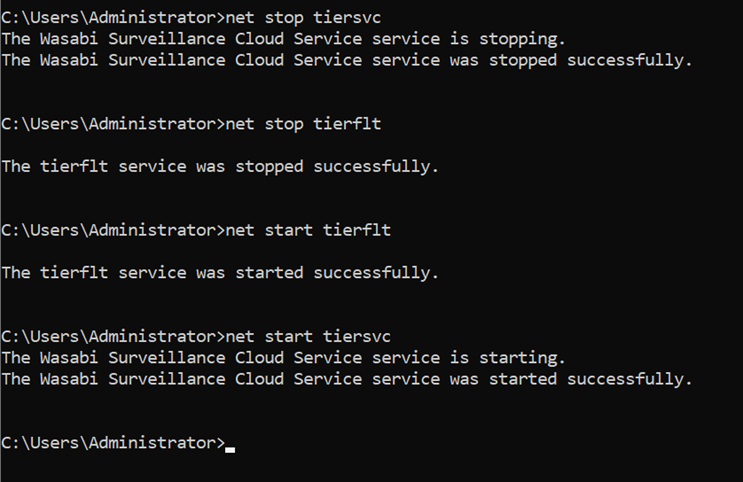
These command lines will restart both the WSC main service and the tiering filter driver, in the correct order.
If the services do not stop or an error occurs, restart the server to refresh the changes.
Once the Windows Explorer window is refreshed, the drive sizes will reflect the changes, as shown below.
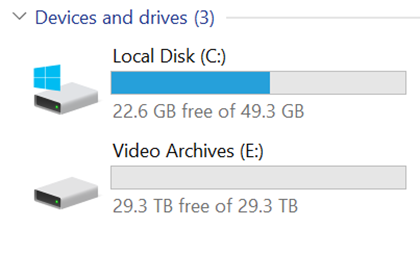
Additionally, verify that the changes are reflected in your VMS software. In the example below, the changes are reflected and the new, available recording storage amount is reported.
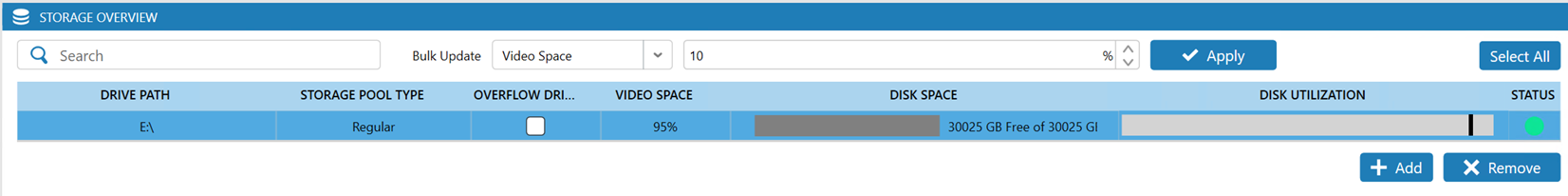
If the changes are not reflected in your VMS, restart the VMS services to refresh the storage reporting.