By pairing your on-premise source with a target (Wasabi bucket), Wasabi Cloud NAS (WCN) serves as a storage bridge and virtual storage unity that displays both your source and bucket data, as if all data were locally stored. 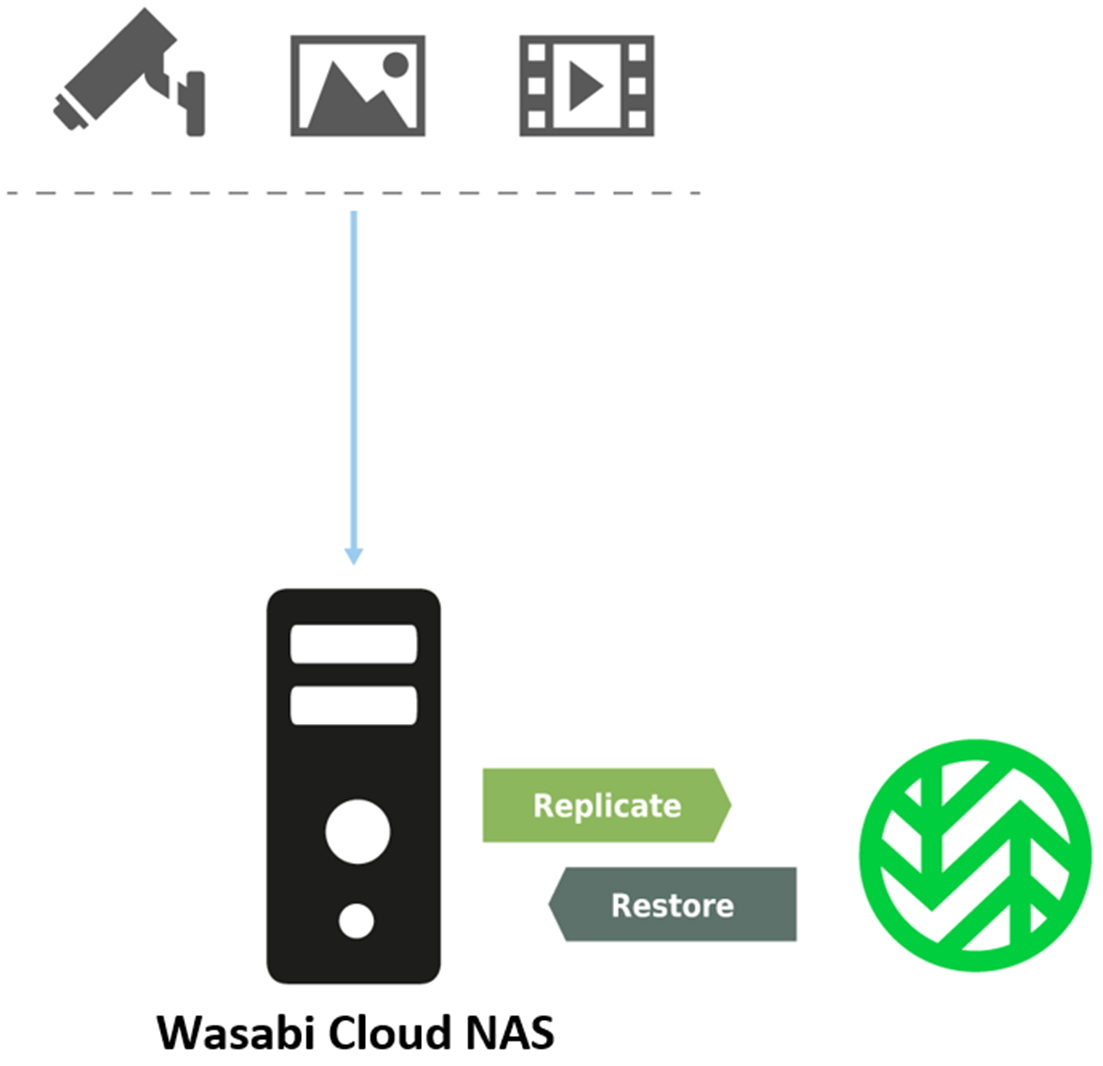
To distribute data between the source and target, you can apply one or more of the following data management mechanisms:
Automatic Data Replication — Copies a file from the source to the bucket.
Space Reclaiming — Creates space on the source by replacing a replicated file with a nearline file.
Active Sync — Synchronizes the contents of multiple sources to a common bucket.
Data Synchronization — Synchronizes the contents of a bucket with a source.
Automatic Data Replication
Automatic Data Replication is a user-defined policy that enables WCN to copy files from the source to the bucket. You can either configure Automatic Data Replication to apply to a specific source-target pair or configure a global policy to apply the policy to all source-target pairs. If needed, you can manually replicate a file or folder from the source to the bucket using the WCN shell extension. While data replication is indispensable for all other data management mechanisms, it can also be used standalone for addressing scenarios such as data backup and disaster recovery. For more information, refer to Configuring Automatic Data Replication.
Space Reclaiming
Automatic Space Reclaiming (Space Reclaiming) is a user-defined policy that enables WCN to free up space on the source by replacing a replicated file with a nearline file. Space Reclaiming is commonly used for the alignment of data with storage costs.
A nearline file is a stub file that looks identical to the original file on the source volume, but neither contains any data nor takes up space on the source. A nearline file points back to the original file and can be retrieved when a user, application, or process attempts to access the file.
With a NAS source, nearline files are located in the control folder and not on the network share. Retrieving a nearline file in the control folder will retrieve it directly on the NAS source.
A stub file is a virtual placeholder that points to the original file that is archived on the source. Stub files are located in a shadow copy folder and act as a gateway between the source and bucket, enabling any automatic or manual retrieval of the nearline file.
An Automatic Space Reclaiming policy can either be assigned to a specific source-target pair or can be configured as a global policy to apply to all source-target pairs. Optionally, you can manually retrieve files and reclaim space using the WCN shell extension. For more detail, refer to Configuring Space Reclaiming.
Active Sync
An Active Sync policy synchronizes the contents of multiple sources (each on a different server) with a common bucket. Sources send and retrieve notifications when data is replicated, modified, or new data is created on another source. When a user or application attempts to access a file, a request is sent to the source(s) containing the file. Upon request, WCN automatically creates nearline files on the source for each new file replicated from another source. Each nearline file can then be retrieved either manually or automatically.
When you configure Active Sync, you can either synchronize the contents across all sources paired with the same bucket or set some sources to update their contents with updates from other sources. Optionally, set WCN to begin retrieving new nearline files immediately after the synchronization process completes. This can be useful when you are synchronizing the contents of a NAS source, as data from other sources will otherwise appear as nearline files in the shadow copy folder for the NAS source.
A common use case for Active Sync is facilitating geo-replication scenarios. For more detail, refer to Configuring Active Sync.
Data Synchronization
Data Synchronization enables you to manually synchronize the contents of a bucket with a source. In the event that WCN detects that a file on the bucket is unavailable on the source, the data synchronization mechanism creates a nearline counterpart for the missing file. Data synchronization can only be processed manually. Manual data synchronization facilitates scenarios involving data migration from one source to another and disaster recovery of data. For more information, refer to Synchronizing Data on the Source and the Bucket.