Objectives for Getting Started
Getting Started with Wasabi Cloud NAS (WCN) provides a quick overview of basic Wasabi features with step-by-step procedures for new and prospective users. Objectives for Getting Started are:
1—Download and install Wasabi Cloud NAS.
2—Activate Wasabi Cloud NAS.
3—Configure Wasabi Cloud NAS.
Accessing Online Help
WCN is a bundle offering of a WCN storage account and the WCN software. To access online help while using your WCN storage account, refer to Accessing Online Help in Getting Started With Wasabi Hot Cloud Storage.
To access online help while using the WCN software:
Click Wasabi Cloud NAS.
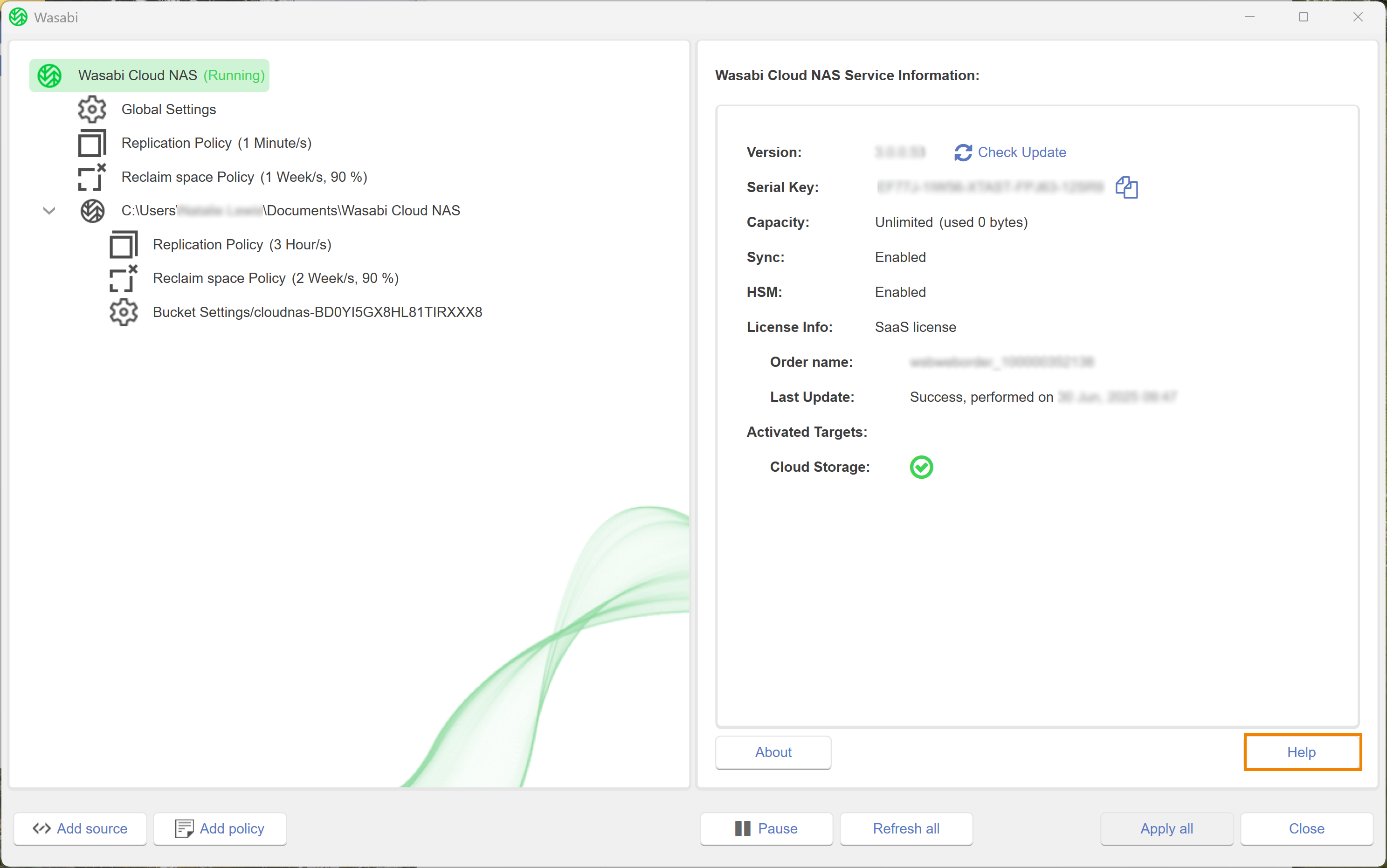
Click Help. You will be redirected to the Wasabi Academy Home page to view user documentation.
Ready to Use Wasabi Cloud NAS?
2—Activate Wasabi Cloud NAS.
3—Configure Wasabi Cloud NAS.
Technical Support
The Wasabi website has the latest product information, including tools to review system status, download software updates, and review support plans. For additional technical support, use this email address to contact a Wasabi Customer Support representative: support@wasabi.com